Page 892 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 892
Chapter 56 Conventional and Molecular Cytogenomic Basis of Hematologic Malignancies 775
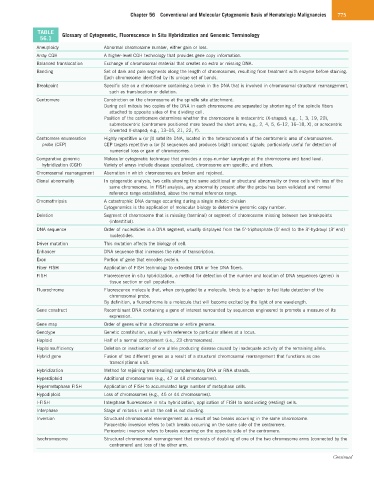
TABLE Glossary of Cytogenetic, Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization and Genomic Terminology
56.1
Aneuploidy Abnormal chromosome number, either gain or loss.
Array CGH A higher-level CGH technology that provides gene copy information.
Balanced translocation Exchange of chromosomal material that creates no extra or missing DNA.
Banding Set of dark and pale segments along the length of chromosomes, resulting from treatment with enzyme before staining.
Each chromosome identified by its unique set of bands.
Breakpoint Specific site on a chromosome containing a break in the DNA that is involved in chromosomal structural rearrangement,
such as translocation or deletion.
Centromere Constriction on the chromosome at the spindle site attachment.
During cell mitosis two copies of the DNA in each chromosome are separated by shortening of the spindle fibers
attached to opposite sides of the dividing cell.
Position of the centromere determines whether the chromosome is metacentric (X-shaped; e.g., 1, 3, 19, 20),
submetacentric (centromere positioned more toward the short arms; e.g., 2, 4, 5, 6–12, 16–18, X), or acrocentric
(inverted V-shaped; e.g., 13–15, 21, 22, Y).
Centromere enumeration Highly repetitive α (or β) satellite DNA, located in the heterochromatin of the centromeric area of chromosomes.
probe (CEP) CEP targets repetitive α (or β) sequences and produces bright compact signals; particularly useful for detection of
numerical loss or gain of chromosomes.
Comparative genomic Molecular cytogenetic technique that provides a copy-number karyotype at the chromosome and band level.
hybridization (CGH) Variety of arrays include disease specialized, chromosome arm specific, and others.
Chromosomal rearrangement Aberration in which chromosomes are broken and rejoined.
Clonal abnormality In cytogenetic analysis, two cells showing the same additional or structural abnormality or three cells with loss of the
same chromosome. In FISH analysis, any abnormality present after the probe has been validated and normal
reference range established, above the normal reference range.
Chromothripsis A catastrophic DNA damage occurring during a single mitotic division
Cytogenomics is the application of molecular biology to determine genomic copy number.
Deletion Segment of chromosome that is missing (terminal) or segment of chromosome missing between two breakpoints
(interstitial).
DNA sequence Order of nucleotides in a DNA segment, usually displayed from the 5′-triphosphate (5′ end) to the 3′-hydroxyl (3′ end)
nucleotides.
Driver mutation This mutation affects the biology of cell.
Enhancer DNA sequence that increases the rate of transcription.
Exon Portion of gene that encodes protein.
Fiber FISH Application of FISH technology to extended DNA or free DNA fibers.
FISH Fluorescence in situ hybridization, a method for detection of the number and location of DNA sequences (genes) in
tissue section or cell population.
Fluorochrome Fluorescence molecule that, when conjugated to a molecule, binds to a hapten to facilitate detection of the
chromosomal probe.
By definition, a fluorochrome is a molecule that will become excited by the light of one wavelength.
Gene construct Recombinant DNA containing a gene of interest surrounded by sequences engineered to promote a measure of its
expression.
Gene map Order of genes within a chromosome or entire genome.
Genotype Genetic constitution, usually with reference to particular alleles at a locus.
Haploid Half of a normal complement (i.e., 23 chromosomes).
Haploinsufficiency Deletion or inactivation of one allele producing disease caused by inadequate activity of the remaining allele.
Hybrid gene Fusion of two different genes as a result of a structural chromosomal rearrangement that functions as one
transcriptional unit.
Hybridization Method for rejoining (reannealing) complementary DNA or RNA strands.
Hyperdiploid Additional chromosomes (e.g., 47 or 48 chromosomes).
Hypermetaphase FISH Application of FISH to accumulated large number of metaphase cells.
Hypodiploid Loss of chromosomes (e.g., 45 or 44 chromosomes).
I-FISH Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization, application of FISH to nondividing (resting) cells.
Interphase Stage of mitosis in which the cell is not dividing.
Inversion Structural chromosomal rearrangement as a result of two breaks occurring in the same chromosome.
Paracentric inversion refers to both breaks occurring on the same side of the centromere.
Pericentric inversion refers to breaks occurring on the opposite side of the centromere.
Isochromosome Structural chromosomal rearrangement that consists of doubling of one of the two chromosome arms (connected by the
centromere) and loss of the other arm.
Continued