Page 897 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 897
780 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
Interphase
Early Prophase
Late Prophase
Interphase
FISH
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Conventional
Cytogenetics
Anaphase
Late Anaphase
Telophase
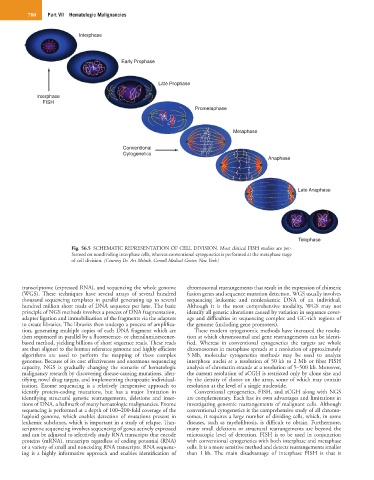
Fig. 56.5 SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF CELL DIVISION. Most clinical FISH studies are per-
formed on nondividing interphase cells, whereas conventional cytogenetics is performed at the metaphase stage
of cell division. (Courtesy Dr. Ari Melnik, Cornell Medical Center, New York.)
transcriptome (expressed RNA), and sequencing the whole genome chromosomal rearrangements that result in the expression of chimeric
(WGS). These techniques have several arrays of several hundred fusion genes and sequence mutation detection. WGS usually involves
thousand sequencing templates in parallel generating up to several sequencing leukemic and nonleukemic DNA of an individual.
hundred million short reads of DNA sequence per lane. The basic Although it is the most comprehensive modality, WGS may not
principle of NGS methods involves a process of DNA fragmentation, identify all genetic alterations caused by variation in sequence cover-
adapter ligation and immobilization of the fragments via the adapters age and difficulties in sequencing complex and GC-rich regions of
to create libraries. The libraries then undergo a process of amplifica- the genome (including gene promoters).
tion, generating multiple copies of each DNA fragment which are These modern cytogenomic methods have increased the resolu-
then sequenced in parallel by a fluorescence- or chemiluminescence- tion at which chromosomal and gene rearrangements can be identi-
based method, yielding billions of short sequence reads. These reads fied. Whereas in conventional cytogenetics the targets are whole
are then aligned to the human reference genome and highly efficient chromosomes in metaphase spreads at a resolution of approximately
algorithms are used to perform the mapping of these complex 5 Mb, molecular cytogenetics methods may be used to analyze
genomes. Because of its cost effectiveness and enormous sequencing interphase nuclei at a resolution of 50 kb to 2 Mb or fiber FISH
capacity, NGS is gradually changing the scenario of hematologic analysis of chromatin strands at a resolution of 5–500 kb. Moreover,
malignancy research by discovering disease-causing mutations, iden- the current resolution of aCGH is restricted only by clone size and
tifying novel drug targets, and implementing therapeutic individual- by the density of clones on the array, some of which may contain
ization. Exome sequencing is a relatively inexpensive approach to resolution at the level of a single nucleotide.
identify protein-coding mutations, but has a major limitation in Conventional cytogenetics, FISH, and aCGH along with NGS
identifying structural genetic rearrangements, deletions and inser- are complementary. Each has its own advantages and limitations in
tions of DNA, a hallmark of many hematologic malignancies. Exome investigating genomic rearrangements of malignant cells. Although
sequencing is performed at a depth of 100–200-fold coverage of the conventional cytogenetics is the comprehensive study of all chromo-
haploid genome, which enables detection of mutations present in somes, it requires a large number of dividing cells, which, in some
leukemic subclones, which is important in a study of relapse. Tran- diseases, such as myelofibrosis, is difficult to obtain. Furthermore,
scriptome sequencing involves sequencing of genes actively expressed many small deletions or structural rearrangements are beyond the
and can be adjusted to selectively study RNA transcripts that encode microscopic level of detection. FISH is to be used in conjunction
proteins (mRNA), transcripts regardless of coding potential (RNA) with conventional cytogenetics with both interphase and metaphase
or a variety of small and noncoding RNA transcripts. RNA sequenc- cells. It is a more sensitive method and detects rearrangements smaller
ing is a highly informative approach and enables identification of than 1 kb. The main disadvantage of interphase FISH is that it