Page 1073 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1073
1048 Part VIII: Monocytes and Macrophages Chapter 67: Structure, Receptors, and Functions of Monocytes and Macrophages 1049
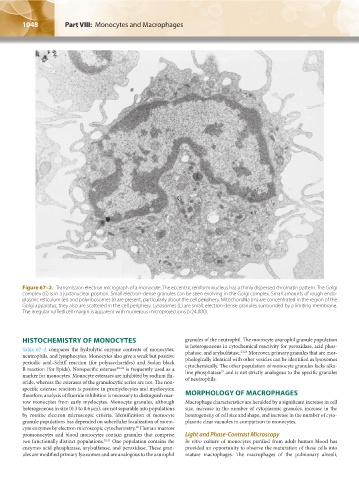
Figure 67–2. Transmission electron micrograph of a monocyte. The eccentric reniform nucleus has a thinly dispersed chromatin pattern. The Golgi
complex (G) is in a juxtanuclear position. Small electron-dense granules can be seen evolving in the Golgi complex. Small amounts of rough endo-
plasmic reticulum (er) and polyribosomes (r) are present, particularly about the cell periphery. Mitochondria (m) are concentrated in the region of the
Golgi apparatus; they also are scattered in the cell periphery. Lysosomes (L) are small, electron-dense granules surrounded by a limiting membrane.
The irregular ruffled cell margin is apparent with numerous microprojections (×24,000).
HISTOCHEMISTRY OF MONOCYTES granules of the neutrophil. The monocyte azurophil granule population
is heterogeneous in cytochemical reactivity for peroxidase, acid phos-
Table 67–2 compares the hydrolytic enzyme contents of monocytes, phatase, and arylsulfatase. 23,24 Moreover, primary granules that are mor-
neutrophils, and lymphocytes. Monocytes also give a weak but positive phologically identical with other vesicles can be identified as lysosomes
periodic acid–Schiff reaction (for polysaccharides) and Sudan black cytochemically. The other population of monocyte granules lacks alka-
B reaction (for lipids). Nonspecific esterase 20–22 is frequently used as a line phosphatase and is not strictly analogous to the specific granules
23
marker for monocytes. Monocyte esterases are inhibited by sodium flu- of neutrophils.
oride, whereas the esterases of the granulocytic series are not. The non-
specific esterase reaction is positive in promyelocytes and myelocytes;
therefore, analysis of fluoride inhibition is necessary to distinguish mar- MORPHOLOGY OF MACROPHAGES
row monocytes from early myelocytes. Monocyte granules, although Macrophage characteristics are heralded by a significant increase in cell
heterogeneous in size (0.3 to 0.6 μm), are not separable into populations size, increase in the number of cytoplasmic granules, increase in the
by routine electron microscopic criteria. Identification of monocyte heterogeneity of cell size and shape, and increase in the number of cyto-
granule populations has depended on subcellular localization of mono- plasmic clear vacuoles in comparison to monocytes.
10
cyte enzymes by electron microscopic cytochemistry. Human marrow
promonocytes and blood monocytes contain granules that comprise Light and Phase-Contrast Microscopy
two functionally distinct populations. 10,11 One population contains the In vitro culture of monocytes purified from adult human blood has
enzymes acid phosphatase, arylsulfatase, and peroxidase. These gran- provided an opportunity to observe the maturation of these cells into
ules are modified primary lysosomes and are analogous to the azurophil mature macrophages. The macrophages of the pulmonary alveoli,
Kaushansky_chapter 67_p1043-1074.indd 1048 9/21/15 10:42 AM