Page 1075 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1075
1050 Part VIII: Monocytes and Macrophages Chapter 67: Structure, Receptors, and Functions of Monocytes and Macrophages 1051
A B
C D
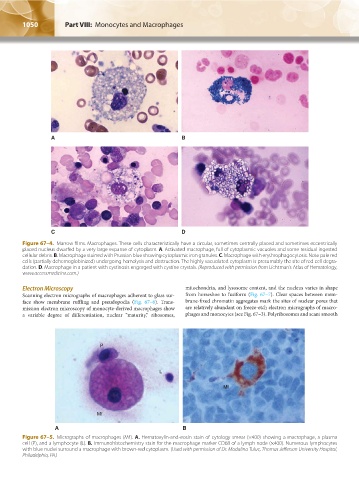
Figure 67–4. Marrow films. Macrophages. These cells characteristically have a circular, sometimes centrally placed and sometimes eccentrically
placed nucleus dwarfed by a very large expanse of cytoplasm. A. Activated macrophage, full of cytoplasmic vacuoles and some residual ingested
cellular debris. B. Macrophage stained with Prussian blue showing cytoplasmic iron granules. C. Macrophage with erythrophagocytosis. Note pale red
cells (partially dehemoglobinized) undergoing hemolysis and destruction. The highly vacuolated cytoplasm is presumably the site of red cell degra-
dation. D. Macrophage in a patient with cystinosis engorged with cystine crystals. (Reproduced with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology,
www.accessmedicine.com.)
Electron Microscopy mitochondria, and lysosome content, and the nucleus varies in shape
Scanning electron micrographs of macrophages adherent to glass sur- from horseshoe to fusiform (Fig. 67–7). Clear spaces between mem-
face show membrane ruffling and pseudopodia (Fig. 67–6). Trans- brane-fixed chromatin aggregates mark the sites of nuclear pores that
mission electron microscopy of monocyte-derived macrophages show are relatively abundant on freeze-etch electron micrographs of macro-
a variable degree of differentiation, nuclear “maturity,” ribosomes, phages and monocytes (see Fig. 67–3). Polyribosomes and scant smooth
P
L
Mf
Mf
A B
Figure 67–5. Micrographs of macrophages (Mf). A. Hematoxylin-and-eosin stain of cytology smear (×400) showing a macrophage, a plasma
cell (P), and a lymphocyte (L). B. Immunohistochemistry stain for the macrophage marker CD68 of a lymph node (×400). Numerous lymphocytes
with blue nuclei surround a macrophage with brown-red cytoplasm. (Used with permission of Dr. Madalina Tuluc, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital,
Philadelphia, PA.)
Kaushansky_chapter 67_p1043-1074.indd 1050 9/21/15 10:42 AM