Page 1074 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1074
1048 Part VIII: Monocytes and Macrophages Chapter 67: Structure, Receptors, and Functions of Monocytes and Macrophages 1049
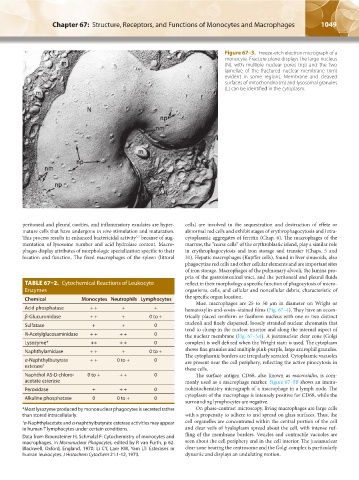
Figure 67–3. Freeze-etch electron micrograph of a
monocyte. Fracture plane displays the large nucleus
(N), with multiple nuclear pores (np) and the two
lamellae of the fractured nuclear membrane (nm)
evident in some regions. Membrane and cleaved
surfaces of mitochondria (m) and lysosomal granules
(L) can be identified in the cytoplasm.
peritoneal and pleural cavities, and inflammatory exudates are hyper- cells) are involved in the sequestration and destruction of effete or
mature cells that have undergone in vivo stimulation and maturation. abnormal red cells and exhibit stages of erythrophagocytosis and intra-
This process results in enhanced bactericidal activity because of aug- cytoplasmic aggregates of ferritin (Chap. 6). The macrophages of the
1,2
mentation of lysosome number and acid hydrolase content. Macro- marrow, the “nurse cells” of the erythroblastic island, play a similar role
phages display attributes of morphologic specialization specific to their in erythrophagocytosis and iron storage and transfer (Chaps. 5 and
location and function. The fixed macrophages of the spleen (littoral 31). Hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cells), found in liver sinusoids, also
phagocytize red cells and other cellular elements and are important sites
of iron storage. Macrophages of the pulmonary alveoli, the lamina pro-
pria of the gastrointestinal tract, and the peritoneal and pleural fluids
TABLE 67–2. Cytochemical Reactions of Leukocyte reflect in their morphology a specific function of phagocytosis of micro-
Enzymes organisms, cells, and cellular and noncellular debris, characteristic of
Chemical Monocytes Neutrophils Lymphocytes the specific organ location.
Most macrophages are 25 to 50 μm in diameter on Wright or
Acid phosphatase + + + + hematoxylin-and-eosin–stained films (Fig. 67–4). They have an eccen-
β-Glucuronidase + + + 0 to + trically placed reniform or fusiform nucleus with one or two distinct
nucleoli and finely dispersed, loosely stranded nuclear chromatin that
Sulfatase + + 0
tend to clump in the nuclear interior and along the internal aspect of
N-Acetylglucosaminidase + + + + 0 the nuclear membrane (Fig. 67–5A). A juxtanuclear clear zone (Golgi
Lysozyme* ++ + + 0 complex) is well defined when the Wright stain is used. The cytoplasm
Naphthylamidase + + + 0 to + shows fine granules and multiple pink-purple, large azurophil granules.
The cytoplasmic borders are irregularly serrated. Cytoplasmic vacuoles
α-Naphthylbutyrate + + 0 to + 0 are present near the cell periphery, reflecting the active pinocytosis in
esterase †
these cells.
Naphthol AS-D chloro- 0 to + + + 0 The surface antigen CD68, also known as macrosialin, is com-
acetate esterase monly used as a macrophage marker. Figure 67–5B shows an immu-
Peroxidase + + + 0 nohistochemistry micrograph of a macrophage in a lymph node. The
cytoplasm of the macrophage is intensely positive for CD68, while the
Alkaline phosphatase 0 0 to + 0
surrounding lymphocytes are negative.
*Most lysozyme produced by mononuclear phagocytes is secreted rather On phase-contrast microscopy, living macrophages are large cells
than stored intracellularly. with a propensity to adhere to and spread on glass surfaces. Thus, the
† α-Naphthylacetate and α-naphthylbutyrate esterase activities may appear cell organelles are concentrated within the central portion of the cell
in human T lymphocytes under certain conditions. and clear veils of hyaloplasm spread about the cell, with intense ruf-
Data from Braunsteiner H, Schmalzl F: Cytochemistry of monocytes and fling of the membrane borders. Vesicles and contractile vacuoles are
macrophages. In Mononuclear Phagocytes, edited by R van Furth, p 62. seen about the cell periphery and in the cell interior. The juxtanuclear
Blackwell, Oxford, England, 1970; Li CY, Lam KW, Yam LT: Esterases in clear zone bearing the centrosome and the Golgi complex is particularly
human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem 21:1-12, 1973. dynamic and displays an undulating motion.
Kaushansky_chapter 67_p1043-1074.indd 1049 9/21/15 10:42 AM