Page 1615 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1615
1590 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 96: Pathology of Lymphomas 1591
Figure 96–3. Same reactive lymph node as in Fig. 96–2 but stained
with an antibody to CD20 (B-cell marker), showing B cells predomi-
nantly localized to the follicles.
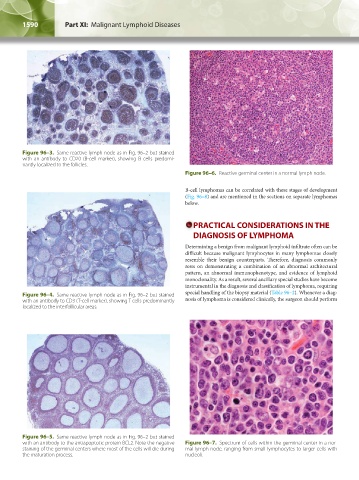
Figure 96–6. Reactive germinal center in a normal lymph node.
B-cell lymphomas can be correlated with these stages of development
(Fig. 96–8) and are mentioned in the sections on separate lymphomas
below.
PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IN THE
DIAGNOSIS OF LYMPHOMA
Determining a benign from malignant lymphoid infiltrate often can be
difficult because malignant lymphocytes in many lymphomas closely
resemble their benign counterparts. Therefore, diagnosis commonly
rests on demonstrating a combination of an abnormal architectural
pattern, an abnormal immunophenotype, and evidence of lymphoid
monoclonality. As a result, several ancillary special studies have become
instrumental in the diagnosis and classification of lymphoma, requiring
Figure 96–4. Same reactive lymph node as in Fig. 96–2 but stained special handling of the biopsy material (Table 96–2). Whenever a diag-
with an antibody to CD3 (T-cell marker), showing T cells predominantly nosis of lymphoma is considered clinically, the surgeon should perform
localized to the interfollicular areas.
Figure 96–5. Same reactive lymph node as in Fig. 96–2 but stained
with an antibody to the antiapoptotic protein BCL2. Note the negative Figure 96–7. Spectrum of cells within the germinal center in a nor-
staining of the germinal centers where most of the cells will die during mal lymph node, ranging from small lymphocytes to larger cells with
the maturation process. nucleoli.
Kaushansky_chapter 96_p1587-1602.indd 1590 9/18/15 6:06 PM