Page 1617 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1617
1592 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 96: Pathology of Lymphomas 1593
or in ruling out a nonhematolymphoid lesion causing lymphadenop-
athy. Although automated flow cytometry can be used in conjunction
with cytologic examination to provide additional information for lym-
phoma diagnosis and classification, tissue biopsy generally is required
before commencement of therapy.
PRECURSOR B- AND T-CELL
LYMPHOMAS/LEUKEMIAS
Lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma represents a malignancy of lym-
phoblasts, either of B or T lineage. They can present in the marrow (leu-
kemia) or with predominant tissue involvement (lymphoma), but they
are considered single-disease entities. Most cases of acute lymphoblastic
leukemia are of B lineage, whereas most cases of lymphoblastic lym-
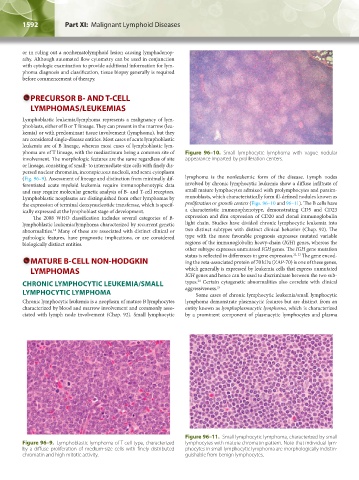
phoma are of T lineage, with the mediastinum being a common site of Figure 96–10. Small lymphocytic lymphoma with vague nodular
involvement. The morphologic features are the same regardless of site appearance imparted by proliferation centers.
or lineage, consisting of small- to intermediate-size cells with finely dis-
persed nuclear chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, and scant cytoplasm
(Fig. 96–9). Assessment of lineage and distinction from minimally dif- lymphoma is the nonleukemic form of the disease. Lymph nodes
ferentiated acute myeloid leukemia require immunophenotypic data involved by chronic lymphocytic leukemia show a diffuse infiltrate of
and may require molecular genetic analysis of B- and T-cell receptors. small mature lymphocytes admixed with prolymphocytes and paraim-
Lymphoblastic neoplasms are distinguished from other lymphomas by munoblasts, which characteristically form ill-defined nodules known as
the expression of terminal deoxynucleotide transferase, which is specif- proliferation or growth centers (Figs. 96–10 and 96–11). The B cells have
ically expressed at the lymphoblast stage of development. a characteristic immunophenotype, demonstrating CD5 and CD23
The 2008 WHO classification includes several categories of B- expression and dim expression of CD20 and clonal immunoglobulin
lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma characterized by recurrent genetic light chain. Studies have divided chronic lymphocytic leukemia into
abnormalities. Many of these are associated with distinct clinical or two distinct subtypes with distinct clinical behavior (Chap. 92). The
14
pathologic features, have prognostic implications, or are considered type with the more favorable prognosis expresses mutated variable
biologically distinct entities. regions of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain (IGH) genes, whereas the
other subtype expresses unmutated IGH genes. The IGH gene mutation
status is reflected in differences in gene expression. 22, 23 The gene encod-
MATURE B-CELL NON-HODGKIN ing the zeta-associated protein of 70 kDa (ZAP-70) is one of these genes,
LYMPHOMAS which generally is expressed by leukemia cells that express unmutated
IGH genes and hence can be used to discriminate between the two sub-
24
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA/SMALL types. Certain cytogenetic abnormalities also correlate with clinical
aggressiveness.
25
LYMPHOCYTIC LYMPHOMA Some cases of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a neoplasm of mature B lymphocytes lymphoma demonstrate plasmacytic features but are distinct from an
characterized by blood and marrow involvement and commonly asso- entity known as lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, which is characterized
ciated with lymph node involvement (Chap. 92). Small lymphocytic by a prominent component of plasmacytic lymphocytes and plasma
Figure 96–11. Small lymphocytic lymphoma, characterized by small
Figure 96–9. Lymphoblastic lymphoma of T-cell type, characterized lymphocytes with mature chromatin pattern. Note that individual lym-
by a diffuse proliferation of medium-size cells with finely distributed phocytes in small lymphocytic lymphoma are morphologically indistin-
chromatin and high mitotic activity. guishable from benign lymphocytes.
Kaushansky_chapter 96_p1587-1602.indd 1592 9/18/15 6:07 PM