Page 1684 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1684
1658 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 100: Mantle Cell Lymphoma 1659
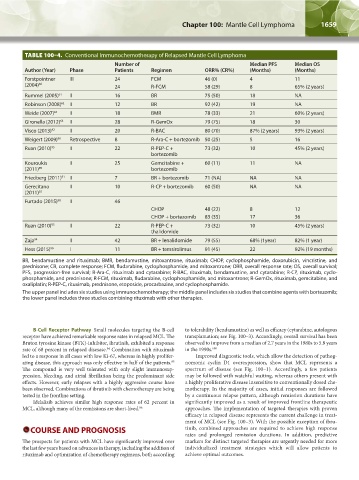
TABLE 100–4. Conventional Immunochemotherapy of Relapsed Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Number of Median PFS Median OS
Author (Year) Phase Patients Regimen ORR% (CR%) (Months) (Months)
Forstpointner III 24 FCM 46 (0) 4 11
(2004) 60 24 R-FCM 58 (29) 8 65% (2 years)
Rummel (2005) 61 II 16 BR 75 (50) 18 NA
Robinson (2008) 62 II 12 BR 92 (42) 19 NA
Weide (2007) 63 II 18 BMR 78 (33) 21 60% (2 years)
Gironella (2012) 64 II 28 R-GemOx 79 (75) 18 30
Visco (2013) 42 II 20 R-BAC 80 (70) 87% (2 years) 93% (2 years)
Weigert (2009) 90 Retrospective 8 R-Ara-C + bortezomib 50 (25) 5 16
Ruan (2010) 95 II 22 R-PEP-C + 73 (32) 10 45% (2 years)
bortezomib
Kouroukis II 25 Gemcitabine + 60 (11) 11 NA
(2011) 89 bortezomib
Friedberg (2011) 91 II 7 BR + bortezomib 71 (NA) NA NA
Gerecitano II 10 R-CP + bortezomib 60 (50) NA NA
(2011) 92
Furtado (2015) 88 II 46
CHOP 48 (22) 8 12
CHOP + bortezomib 83 (35) 17 36
Ruan (2010) 95 II 22 R-PEP-C + 73 (32) 10 45% (2 years)
thalidomide
Zaja 94 II 42 BR + lenalidomide 79 (55) 68% (1year) 82% (1 year)
Hess (2015) 96 I 11 BR + temsirolimus 91 (45) 22 92% (19 months)
BR, bendamustine and rituximab; BMR, bendamustine, mitoxantrone, rituximab; CHOP, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and
prednisone; CR, complete response; FCM, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and mitoxantrone; ORR, overall response rate; OS, overall survival;
PFS, progression-free survival; R-Ara-C, rituximab and cytarabine; R-BAC, rituximab, bendamustine, and cytarabine; R-CP, rituximab, cyclo-
phosphamide, and prednisone; R-FCM, rituximab, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and mitoxantrone; R-GemOx, rituximab, gemcitabine, and
oxaliplatin; R-PEP-C, rituximab, prednisone, etoposide, procarbazine, and cyclophosphamide.
The upper panel includes six studies using immunochemotherapy; the middle panel includes six studies that combine agents with bortezomib;
the lower panel includes three studies combining rituximab with other therapies.
B-Cell Receptor Pathway Small molecules targeting the B-cell to tolerability (bendamustine) as well as efficacy (cytarabine, autologous
receptor have achieved remarkable response rates in relapsed MCL. The transplantation; see Fig. 100–3). Accordingly, overall survival has been
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)-inhibitor, ibrutinib, exhibited a response observed to improve from a median of 2.7 years in the 1980s to 5.8 years
84
rate of 68 percent in relapsed disesase. Combination with rituximab in the 1990s. 100
led to a response in all cases with low Ki-67, whereas in highly prolifer- Improved diagnostic tools, which allow the detection of pathog-
ating disease, this approach was only effective in half of the patients. nomonic cyclin D1 overexpression, show that MCL represents a
85
The compound is very well tolerated with only slight immunosup- spectrum of disease (see Fig. 100–1). Accordingly, a few patients
pression, bleeding, and atrial fibrillation being the predominant side may be followed with watchful waiting, whereas others present with
effects. However, early relapses with a highly aggressive course have a highly proliferative disease insensitive to conventionally dosed che-
been observed. Combinations of ibrutinib with chemotherapy are being motherapy. In the majority of cases, initial responses are followed
tested in the frontline setting. by a continuous relapse pattern, although remission durations have
Idelalisib achieves similar high response rates of 62 percent in significantly improved as a result of improved frontline therapeutic
MCL, although many of the remissions are short-lived. 86 approaches. The implementation of targeted therapies with proven
efficacy in relapsed disease represents the current challenge in treat-
ment of MCL (see Fig. 100–3). With the possible exception of ibru-
COURSE AND PROGNOSIS tinib, combined approaches are required to achieve high response
rates and prolonged remission durations. In addition, predictive
The prospects for patients with MCL have significantly improved over markers for distinct targeted therapies are urgently needed for more
the last few years based on advances in therapy, including the addition of individualized treatment strategies which will allow patients to
rituximab and optimization of chemotherapy regimens, both according achieve optimal outcomes.
Kaushansky_chapter 100_p1653-1662.indd 1659 9/18/15 5:06 PM