Page 1964 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1964
1938 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 113: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of the Coagulation Factors 1939
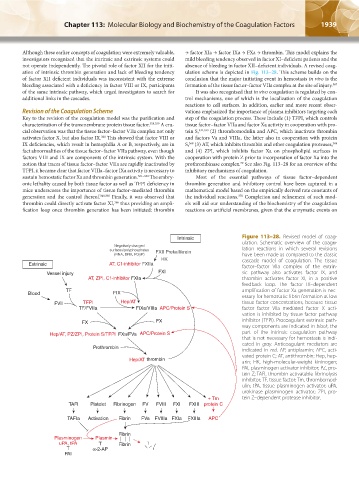
Although these earlier concepts of coagulation were extremely valuable, → factor XIa → factor IXa → FXa → thrombin. This model explains the
investigators recognized that the intrinsic and extrinsic systems could mild bleeding tendency observed in factor XI–deficient patients and the
not operate independently. The pivotal role of factor XII for the initi- absence of bleeding in factor XII–deficient individuals. A revised coag-
ation of intrinsic thrombin generation and lack of bleeding tendency ulation scheme is depicted in Fig. 113–28. This scheme builds on the
of factor XII deficient individuals was inconsistent with the extreme conclusion that the major initiating event in hemostasis in vivo is the
bleeding associated with a deficiency in factor VIII or IX, participants formation of the tissue factor–factor VIIa complex at the site of injury. 367
of the same intrinsic pathway, which urged investigators to search for It was also recognized that in vivo coagulation is regulated by con-
additional links in the cascades. trol mechanisms, one of which is the localization of the coagulation
reactions to cell surfaces. In addition, earlier and more recent obser-
Revision of the Coagulation Scheme vations emphasized the importance of plasma inhibitors targeting each
Key to the revision of the coagulation model was the purification and step of the coagulation process. These include (1) TFPI, which controls
characterization of the transmembrane protein tissue factor. 358,359 A cru- tissue factor–factor VIIa and factor Xa activity in cooperation with pro-
cial observation was that the tissue factor–factor VIIa complex not only tein S, 331,333 (2) thrombomodulin and APC, which inactivate thrombin
360
activates factor X, but also factor IX. This showed that factor VIII or and factors Va and VIIIa, the latter also in cooperation with protein
369
368
IX deficiencies, which result in hemophilia A or B, respectively, are in S, (3) AT, which inhibits thrombin and other coagulation proteases,
fact abnormalities of the tissue factor–factor VIIa pathway, even though and (4) ZPI, which inhibits factor Xa on phospholipid surfaces in
factors VIII and IX are components of the intrinsic system. With the cooperation with protein Z prior to incorporation of factor Xa into the
79
notion that traces of tissue factor–factor VIIa are rapidly inactivated by prothrombinase complex. See also Fig. 113–28 for an overview of the
TFPI, it became clear that factor VIIIa–factor IXa activity is necessary to inhibitory mechanisms of coagulation.
sustain hemostatic factor Xa and thrombin generation. 361–364 The embry- Most of the essential pathways of tissue factor–dependent
onic lethality caused by both tissue factor as well as TFPI deficiency in thrombin generation and inhibitory control have been captured in a
mice underscores the importance of tissue factor–mediated thrombin mathematical model based on the empirically derived rate constants of
370
generation and the control thereof. 340,365 Finally, it was observed that the individual reactions. Completion and refinement of such mod-
thrombin could directly activate factor XI, thus providing an ampli- els will aid our understanding of the biochemistry of the coagulation
366
fication loop once thrombin generation has been initiated: thrombin reactions on artificial membranes, given that the enzymatic events on
Intrinsic Figure 113–28. Revised model of coag-
ulation. Schematic overview of the coagu-
Negatively-charged
surfaces/polyphosphates FXII Prekallikrein lation reactions in which several revisions
(RNA, DNA, PolyP) have been made as compared to the classic
HK cascade model of coagulation. The tissue
Extrinsic AT, C1-inhibitor FXIIa factor–factor VIIa complex of the extrin-
Vessel injury FXI sic pathway also activates factor IX, and
AT, ZPI, C1-inhibitor FXIa thrombin activates factor XI, in a positive
feedback loop. The factor IX–dependent
TF amplification of factor Xa generation is nec-
Blood FIX
essary for hemostatic fibrin formation at low
FVII TFPI Hep/AT tissue factor concentrations, because tissue
TF/FVIIa FIXa/VIIIa APC/Protein S factor–factor VIIa–mediated factor X acti-
vation is inhibited by tissue factor pathway
FX FX inhibitor (TFPI). Procoagulant extrinsic path-
way components are indicated in black, the
Hep/AT, PZ/ZPI, Protein S/TFPI FXa/FVa APC/Protein S part of the intrinsic coagulation pathway
that is not necessary for hemostasis is indi-
cated in gray. Anticoagulant mediators are
Prothrombin indicated in red. AP, antiplasmin; APC, acti-
vated protein C; AT, antithrombin; Hep, hep-
Hep/AT thrombin arin; HK, high-molecular-weight kininogen;
PAI, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PZ, pro-
tein Z; TAFI, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis
inhibitor; TF, tissue factor; Tm, thrombomod-
ulin; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; uPA,
urokinase plasminogen activator; ZPI, pro-
+ Tm tein Z–dependent protease inhibitor.
TAFI Platelet Fibrinogen FV FVIII FXI FXIII protein C
TAFIa Activation Fibrin FVa FVIIIa FXIa FXIIIa APC
Fibrin
Plasminogen Plasmin
uPA, tPA T Fibrin
T α-2-AP
PAI
Kaushansky_chapter 113_p1915-1948.indd 1939 9/21/15 2:40 PM