Page 249 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 249
224 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 225
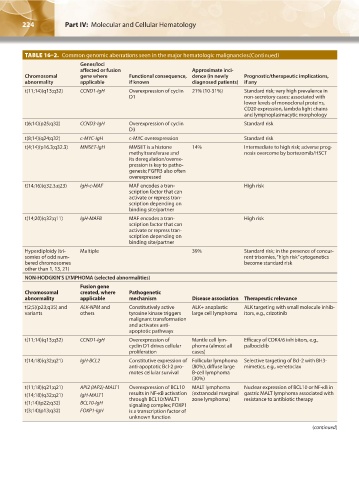
TABLE 16–2. Common genomic aberrations seen in the major hematologic malignancies.(Continued)
Genes/loci
affected or fusion Approximate inci-
Chromosomal gene where Functional consequence, dence (in newly Prognostic/therapeutic implications,
abnormality applicable if known diagnosed patients) if any
t(11;14)(q13;q32) CCND1-IgH Overexpression of cyclin 21% (10-31%) Standard risk; very high prevalence in
D1 non-secretory cases; associated with
lower levels of monoclonal proteins,
CD20 expression, lambda light chains
and lymphoplasmacytic morphology
t(6;14)(p25;q32) CCND3-IgH Overexpression of cyclin Standard risk
D3
t(8;14)(q24;q32) c-MYC-IgH c-MYC overexpression Standard risk
t(4;14)(p16.3;q32.3) MMSET-IgH MMSET is a histone 14% Intermediate to high risk; adverse prog-
methyltransferase and nosis overcome by bortezomib/HSCT
its deregulation/overex-
pression is key to patho-
genesis; FGFR3 also often
overexpressed
t(14;16)(q32.3;q23) IgH-c-MAF MAF encodes a tran- High risk
scription factor that can
activate or repress tran-
scription depending on
binding site/partner
t(14;20)(q32;q11) IgH-MAFB MAF encodes a tran- High risk
scription factor that can
activate or repress tran-
scription depending on
binding site/partner
Hyperdiploidy (tri- Multiple 39% Standard risk; in the presence of concur-
somies of odd num- rent trisomies, “high risk” cytogenetics
bered chromosomes become standard risk
other than 1, 13, 21)
NON-HODGKIN’S LYMPHOMA (selected abnormalities)
Fusion gene
Chromosomal created, where Pathogenetic
abnormality applicable mechanism Disease association Therapeutic relevance
t(2;5)(p23;q35) and ALK-NPM and Constitutively active ALK+ anaplastic ALK targeting with small molecule inhib-
variants others tyrosine kinase triggers large cell lymphoma itors, e.g., crizotinib
malignant transformation
and activates anti-
apoptotic pathways
t(11;14)(q13;q32) CCND1-IgH Overexpression of Mantle cell lym- Efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitors, e.g.,
cyclin D1 drives cellular phoma (almost all palbociclib
proliferation cases)
t(14;18)(q32;q21) IgH-BCL2 Constitutive expression of Follicular lymphoma Selective targeting of Bcl-2 with BH3-
anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 pro- (80%), diffuse large mimetics, e.g., venetoclax
motes cellular survival B-cell lymphoma
(30%)
t(11;18)(q21;q21) API2 (IAP2)-MALT1 Overexpression of BCL10 MALT lymphoma Nuclear expression of BCL10 or NF-κB in
t(14;18)(q32;q21) IgH-MALT1 results in NF-κB activation (extranodal marginal gastric MALT lymphoma associated with
t(1;14)(p22;q32) BCL10-IgH through BCL10/MALT1 zone lymphoma) resistance to antibiotic therapy
signaling complex; FOXP1
t(3;14)(p13;q32) FOXP1-IgH is a transcription factor of
unknown function
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 224 9/18/15 11:57 PM