Page 248 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 248
222 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 223
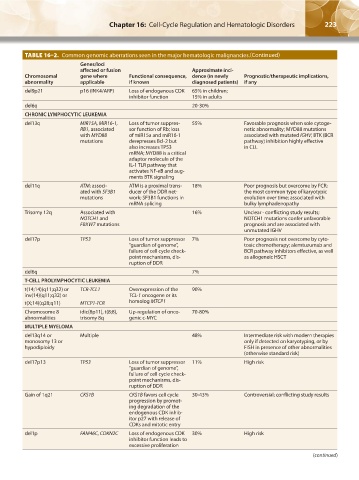
TABLE 16–2. Common genomic aberrations seen in the major hematologic malignancies.(Continued)
Genes/loci
affected or fusion Approximate inci-
Chromosomal gene where Functional consequence, dence (in newly Prognostic/therapeutic implications,
abnormality applicable if known diagnosed patients) if any
del9p21 p16 (INK4/ARF) Loss of endogenous CDK 65% in children;
inhibitor function 15% in adults
del6q 20-30%
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
del13q MIR15A, MIR16-1, Loss of tumor suppres- 55% Favorable prognosis when sole cytoge-
RB1, associated sor function of Rb; loss netic abnormality; MYD88 mutations
with MYD88 of miR15a and miR16-1 associated with mutated IGHV; BTK (BCR
mutations derepresses Bcl-2 but pathway) inhibition highly effective
also increases TP53 in CLL
mRNA; MYD88 is a critical
adaptor molecule of the
IL-1 TLR pathway that
activates NF-κB and aug-
ments BTK signaling
del11q ATM; associ- ATM is a proximal trans- 18% Poor prognosis but overcome by FCR;
ated with SF3B1 ducer of the DDR net- the most common type of karyotypic
mutations work; SF3B1 functions in evolution over time; associated with
mRNA splicing bulky lymphadenopathy
Trisomy 12q Associated with 16% Unclear - conflicting study results;
NOTCH1 and NOTCH1 mutations confer unfavorable
FBXW7 mutations prognosis and are associated with
unmutated IGHV
del17p TP53 Loss of tumor suppressor 7% Poor prognosis not overcome by cyto-
“guardian of genome”, toxic chemotherapy; alemtuzumab and
failure of cell cycle check- BCR pathway inhibitors effective, as well
point mechanisms, dis- as allogeneic HSCT
ruption of DDR
del6q 7%
T-CELL PROLYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
t(14;14)(q11;q32) or TCR-TCL1 Overexpression of the 90%
inv(14)(q11;q32) or TCL-1 oncogene or its
t(X;14)(q28;q11) MTCP1-TCR homolog MTCP1
Chromosome 8 idic(8p11), t(8;8), Up-regulation of onco- 70-80%
abnormalities trisomy 8q genic c-MYC
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
del13q14 or Multiple 48% Intermediate risk with modern therapies
monosomy 13 or only if detected on karyotyping, or by
hypodiploidy FISH in presence of other abnormalities
(otherwise standard risk)
del17p13 TP53 Loss of tumor suppressor 11% High risk
“guardian of genome”,
failure of cell cycle check-
point mechanisms, dis-
ruption of DDR
Gain of 1q21 CKS1B CKS1B favors cell cycle 30-43% Controversial; conflicting study results
progression by promot-
ing degradation of the
endogenous CDK inhib-
itor p27 with release of
CDKs and mitotic entry
del1p FAM46C, CDKN2C Loss of endogenous CDK 30% High risk
inhibitor function leads to
excessive proliferation
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 223 9/18/15 11:57 PM