Page 251 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 251
226 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 227
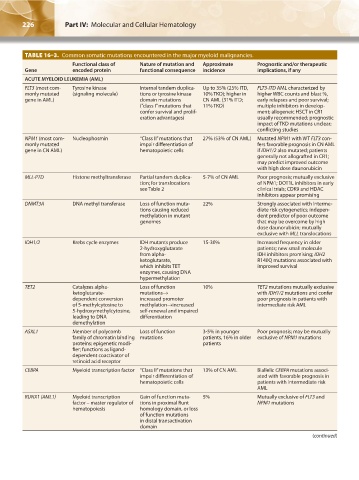
TABLE 16–3. Common somatic mutations encountered in the major myeloid malignancies.
Functional class of Nature of mutation and Approximate Prognostic and/or therapeutic
Gene encoded protein functional consequence incidence implications, if any
ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA (AML)
FLT3 (most com- Tyrosine kinase Internal tandem duplica- Up to 35% (25% ITD, FLT3-ITD AML characterized by
monly mutated (signaling molecule) tions or tyrosine kinase 10% TKD); higher in higher WBC counts and blast %,
gene in AML) domain mutations CN AML (31% ITD; early relapses and poor survival;
(“class I” mutations that 11% TKD) multiple inhibitors in develop-
confer survival and prolif- ment; allogeneic HSCT in CR1
eration advantages) usually recommended; prognostic
impact of TKD mutations unclear;
conflicting studies
NPM1 (most com- Nucleophosmin “Class II” mutations that 27% (53% of CN AML) Mutated NPM1 with WT FLT3 con-
monly mutated impair differentiation of fers favorable prognosis in CN AML
gene in CN AML) hematopoietic cells if IDH1/2 also mutated; patients
generally not allografted in CR1;
may predict improved outcome
with high dose daunorubicin
MLL-PTD Histone methyltransferase Partial tandem duplica- 5-7% of CN AML Poor prognosis; mutually exclusive
tion; for translocations of NPM1; DOT1L inhibitors in early
see Table 2 clinical trials; CDK9 and HDAC
inhibitors appear promising
DNMT3A DNA methyl transferase Loss of function muta- 22% Strongly associated with interme-
tions causing reduced diate risk cytogenetics; indepen-
methylation in mutant dent predictor of poor outcome
genomes that may be overcome by high
dose daunorubicin; mutually
exclusive with MLL translocations
IDH1/2 Krebs cycle enzymes IDH mutants produce 15-30% Increased frequency in older
2-hydroxyglutarate patients; new small molecule
from alpha- IDH inhibitors promising; IDH2
ketoglutarate, R140Q mutations associated with
which inhibits TET improved survival
enzymes, causing DNA
hypermethylation
TET2 Catalyzes alpha- Loss of function 10% TET2 mutations mutually exclusive
ketoglutarate- mutations→ with IDH1/2 mutations and confer
dependent conversion increased promoter poor prognosis in patients with
of 5-methylcytosine to methylation→increased intermediate risk AML
5-hydroxymethylcytosine, self-renewal and impaired
leading to DNA differentiation
demethylation
ASXL1 Member of polycomb Loss of function 3-5% in younger Poor prognosis; may be mutually
family of chromatin binding mutations patients, 16% in older exclusive of NPM1 mutations
proteins; epigenetic modi- patients
fier; functions as ligand-
dependent coactivator of
retinoid acid receptor
CEBPA Myeloid transcription factor “Class II” mutations that 13% of CN AML Biallelic CEBPA mutations associ-
impair differentiation of ated with favorable prognosis in
hematopoietic cells patients with intermediate risk
AML
RUNX1 (AML1) Myeloid transcription Gain of function muta- 5% Mutually exclusive of FLT3 and
factor – master regulator of tions in proximal Runt NPM1 mutations
hematopoiesis homology domain, or loss
of function mutations
in distal transactivation
domain
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 226 9/18/15 11:57 PM