Page 253 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 253
228 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 229
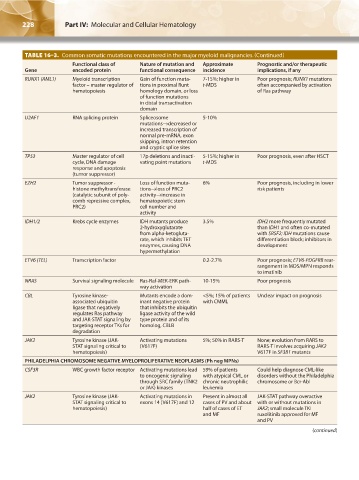
TABLE 16–3. Common somatic mutations encountered in the major myeloid malignancies.(Continued)
Functional class of Nature of mutation and Approximate Prognostic and/or therapeutic
Gene encoded protein functional consequence incidence implications, if any
RUNX1 (AML1) Myeloid transcription Gain of function muta- 7-15%; higher in Poor prognosis; RUNX1 mutations
factor – master regulator of tions in proximal Runt t-MDS often accompanied by activation
hematopoiesis homology domain, or loss of Ras pathway
of function mutations
in distal transactivation
domain
U2AF1 RNA splicing protein Spliceosome 5-10%
mutations→decreased or
increased transcription of
normal pre-mRNA, exon
skipping, intron retention
and cryptic splice sites
TP53 Master regulator of cell 17p deletions and inacti- 5-15%; higher in Poor prognosis, even after HSCT
cycle, DNA damage vating point mutations t-MDS
response and apoptosis
(tumor suppressor)
EZH2 Tumor suppressor - Loss of function muta- 6% Poor prognosis, including in lower
histone methyltransferase tions→loss of PRC2 risk patients
(catalytic subunit of poly- activity→increase in
comb repressive complex, hematopoietic stem
PRC2) cell number and
activity
IDH1/2 Krebs cycle enzymes IDH mutants produce 3.5% IDH2 more frequently mutated
2-hydroxyglutarate than IDH1 and often co-mutated
from alpha-ketogluta- with SRSF2; IDH mutations cause
rate, which inhibits TET differentiation block; inhibitors in
enzymes, causing DNA development
hypermethylation
ETV6 (TEL) Transcription factor 0.2-2.7% Poor prognosis; ETV6-PDGFRB rear-
rangement in MDS/MPN responds
to imatinib
NRAS Survival signaling molecule Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK path- 10-15% Poor prognosis
way activation
CBL Tyrosine kinase- Mutants encode a dom- <5%; 15% of patients Unclear impact on prognosis
associated ubiquitin inant negative protein with CMML
ligase that negatively that inhibits the ubiquitin
regulates Ras pathway ligase activity of the wild
and JAK-STAT signaling by type protein and of its
targeting receptor TKs for homolog, CBLB
degradation
JAK2 Tyrosine kinase (JAK- Activating mutations 5%; 50% in RARS-T None; evolution from RARS to
STAT signaling critical to (V617F) RARS-T involves acquiring JAK2
hematopoiesis) V617F in SF3B1 mutants
PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME NEGATIVE MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASMS (Ph neg MPNs)
CSF3R WBC growth factor receptor Activating mutations lead 59% of patients Could help diagnose CML-like
to oncogenic signaling with atypical CML or disorders without the Philadelphia
through SRC family (TNK2 chronic neutrophilic chromosome or Bcr-Abl
or JAK) kinases leukemia
JAK2 Tyrosine kinase (JAK- Activating mutations in Present in almost all JAK-STAT pathway overactive
STAT signaling critical to exons 14 (V617F) and 12 cases of PV and about with or without mutations in
hematopoiesis) half of cases of ET JAK2; small molecule TKI
and MF ruxolitinib approved for MF
and PV
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 228 9/18/15 11:57 PM