Page 497 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 497
472 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 31: Structure and Composition of the Erythrocyte 473
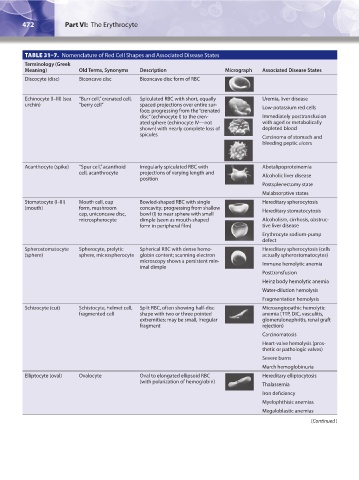
TABLE 31–7. Nomenclature of Red Cell Shapes and Associated Disease States
Terminology (Greek
Meaning) Old Terms, Synonyms Description Micrograph Associated Disease States
Discocyte (disc) Biconcave disc Biconcave disc form of RBC
Echinocyte (I–III) (sea “Burr cell,” crenated cell, Spiculated RBC with short, equally Uremia, liver disease
urchin) “berry cell” spaced projections over entire sur- Low-potassium red cells
face; progressing from the “crenated
disc” (echinocyte I) to the cren- Immediately posttransfusion
ated sphere (echinocyte IV—not with aged or metabolically
shown) with nearly complete loss of depleted blood
spicules Carcinoma of stomach and
bleeding peptic ulcers
Acanthocyte (spike) “Spur cell,” acanthoid Irregularly spiculated RBC with Abetalipoproteinemia
cell, acanthrocyte projections of varying length and Alcoholic liver disease
position
Postsplenectomy state
Malabsorptive states
Stomatocyte (I–III) Mouth cell, cup Bowled-shaped RBC with single Hereditary spherocytosis
(mouth) form, mushroom concavity; progressing from shallow Hereditary stomatocytosis
cap, uniconcave disc, bowl (I) to near sphere with small
microspherocyte dimple (seen as mouth-shaped Alcoholism, cirrhosis, obstruc-
form in peripheral film) tive liver disease
Erythrocyte sodium-pump
defect
Spherostomatocyte Spherocyte, prelytic Spherical RBC with dense hemo- Hereditary spherocytosis (cells
(sphere) sphere, microspherocyte globin content; scanning electron actually spherostomatocytes)
microscopy shows a persistent min- Immune hemolytic anemia
imal dimple
Posttransfusion
Heinz body hemolytic anemia
Water-dilution hemolysis
Fragmentation hemolysis
Schizocyte (cut) Schistocyte, helmet cell, Split RBC, often showing half-disc Microangiopathic hemolytic
fragmented cell shape with two or three pointed anemia (TTP, DIC, vasculitis,
extremities; may be small, irregular glomerulonephritis, renal graft
fragment rejection)
Carcinomatosis
Heart-valve hemolysis (pros-
thetic or pathologic valves)
Severe burns
March hemoglobinuria
Elliptocyte (oval) Ovalocyte Oval to elongated ellipsoid RBC Hereditary elliptocytosis
(with polarization of hemoglobin)
Thalassemia
Iron deficiency
Myelophthisic anemias
Megaloblastic anemias
(Continued )
Kaushansky_chapter 31_p0459-0478.indd 472 9/18/15 10:59 PM