Page 646 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 646
620 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 42: Iron Metabolism 621
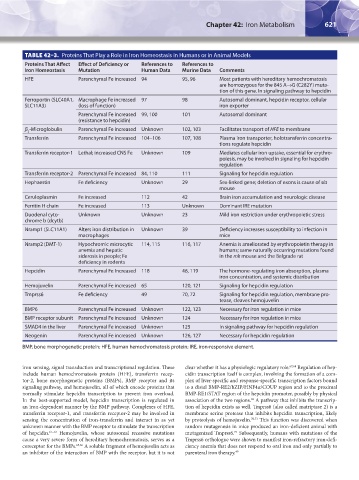
TABLE 42–3. Proteins That Play a Role in Iron Homeostasis in Humans or in Animal Models
Proteins That Affect Effect of Deficiency or References to References to
Iron Homeostasis Mutation Human Data Murine Data Comments
HFE Parenchymal Fe increased 94 95, 96 Most patients with hereditary hemochromatosis
are homozygous for the 845 A→G (C282Y) muta-
tion of this gene. In signaling pathway to hepcidin
Ferroportin (SLC40A1, Macrophage Fe increased 97 98 Autosomal dominant, hepcidin receptor, cellular
SLC11A3) (loss of function) iron exporter
Parenchymal Fe increased 99, 100 101 Autosomal dominant
(resistance to hepcidin)
β -Microglobulin Parenchymal Fe increased Unknown 102, 103 Facilitates transport of HFE to membrane
2
Transferrin Parenchymal Fe increased 104–106 107, 108 Plasma iron transporter, holotransferrin concentra-
tions regulate hepcidin
Transferrin receptor-1 Lethal; increased CNS Fe Unknown 109 Mediates cellular iron uptake, essential for erythro-
poiesis, may be involved in signaling for hepcidin
regulation
Transferrin receptor-2 Parenchymal Fe increased 84, 110 111 Signaling for hepcidin regulation
Hephaestin Fe deficiency Unknown 29 Sex-linked gene; deletion of exons is cause of sla
mouse
Ceruloplasmin Fe increased 112 42 Brain iron accumulation and neurologic disease
Ferritin H chain Fe increased 113 Unknown Dominant IRE mutation
Duodenal cyto- Unknown Unknown 23 Mild iron restriction under erythropoietic stress
chrome b (dcytb)
Nramp1 (SLC11A1) Alters iron distribution in Unknown 39 Deficiency increases susceptibility to infection in
macrophages mice
Nramp2 (DMT-1) Hypochromic microcytic 114, 115 116, 117 Anemia is ameliorated by erythropoietin therapy in
anemia and hepatic humans; same naturally occurring mutations found
siderosis in people; Fe in the mk mouse and the Belgrade rat
deficiency in rodents
Hepcidin Parenchymal Fe Increased 118 46, 119 The hormone-regulating iron absorption, plasma
iron concentration, and systemic distribution
Hemojuvelin Parenchymal Fe increased 65 120, 121 Signaling for hepcidin regulation
Tmprss6 Fe deficiency 49 70, 72 Signaling for hepcidin regulation, membrane pro-
tease, cleaves hemojuvelin
BMP6 Parenchymal Fe increased Unknown 122, 123 Necessary for iron regulation in mice
BMP receptor subunit Parenchymal Fe increased Unknown 124 Necessary for iron regulation in mice
SMAD4 in the liver Parenchymal Fe increased Unknown 125 In signaling pathway for hepcidin regulation
Neogenin Parenchymal Fe increased Unknown 126, 127 Necessary for hepcidin regulation
BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; HFE, human hemochromatosis protein; IRE, iron-responsive element.
iron sensing, signal transduction and transcriptional regulation. These clear whether it has a physiologic regulatory role. 67,68 Regulation of hep-
include human hemochromatosis protein (HFE), transferrin recep- cidin transcription itself is complex, involving the formation of a com-
tor-2, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), BMP receptor and its plex of liver-specific and response-specific transcription factors bound
signaling pathway, and hemojuvelin, all of which encode proteins that to a distal BMP-RE2/bZIP/HNF4α/COUP region and to the proximal
normally stimulate hepcidin transcription to prevent iron overload. BMP-RE1/STAT region of the hepcidin promoter, possibly by physical
In the best-supported model, hepcidin transcription is regulated in association of the two regions. A pathway that inhibits the transcrip-
69
an iron-dependent manner by the BMP pathway. Complexes of HFE, tion of hepcidin exists as well. Tmprss6 (also called matriptase 2) is a
transferrin receptor-1, and transferrin receptor-2 may be involved in membrane serine protease that inhibits hepcidin transcription, likely
sensing the concentration of iron-transferrin and interact in as yet by proteolysis of hemojuvelin. 70,71 This function was discovered when
unknown manner with the BMP receptor to stimulate the transcription random mutagenesis in mice produced an iron-deficient animal with
72
of hepcidin. 61–64 Hemojuvelin, whose autosomal recessive mutations mutagenized Tmprss6. Subsequently, humans with mutations of the
cause a very severe form of hereditary hemochromatosis, serves as a Tmprss6 orthologue were shown to manifest iron-refractory iron-defi-
coreceptor for the BMPs. 65,66 A soluble fragment of hemojuvelin acts as ciency anemia that does not respond to oral iron and only partially to
an inhibitor of the interaction of BMP with the receptor, but it is not parenteral iron therapy. 49
Kaushansky_chapter 42_p0617-0626.indd 621 9/17/15 6:26 PM