Page 762 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 762
736 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 48: The Thalassemias: Disorders of Globin Synthesis 737
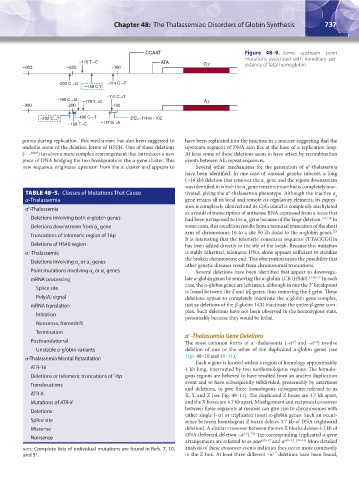
CCAAT Figure 48–9. Some upstream point
mutations associated with hereditary per-
–175 T→C ATA Gγ sistence of fetal hemoglobin.
–300 –200 –100
–202 C→G –114 C→T
–158 C T
–114 C→T
–195 C→G –175 T→C Aγ
–300 –200 –100
–202 C→T –196 C→T DEL–114 to –102
–198 T→C –117 G→A
points during replication. This mechanism has also been suggested to have been replicated into the junction in a manner suggesting that the
underlie some of the deletion forms of HPFH. One of these deletions upstream segment of DNA also lies at the base of a replication loop.
(– – MED ) involves a more complex rearrangement that introduces a new At least some of these deletions seem to have arisen by recombination
piece of DNA bridging the two breakpoints in the α-gene cluster. This events between Alu repeat sequences.
new sequence originates upstream from the α cluster and appears to Several other mechanisms for the generation of α -thalassemia
0
have been identified. In one case of unusual genetic interest, a long
(>18 kb) deletion that removes the α gene and the region downstream
1
was identified in which the α gene remains intact but is completely inac-
2
TABLE 48–5. Classes of Mutations That Cause tivated, giving the α -thalassemia phenotype. Although the inactive α
0
2
α-Thalassemia gene retains all its local and remote cis-regulatory elements, its expres-
α -Thalassemia sion is completely silenced and its CpG island is completely methylated
0
as a result of transcription of antisense RNA expressed from a locus that
Deletions involving both α-globin genes had been juxtaposed to the α gene because of the large deletion. 133,134 In
2
Deletions downstream from α gene some cases, this condition results from a terminal truncation of the short
2 135
Truncations of telomeric region of 16p arm of chromosome 16 to a site 50 kb distal to the α-globin genes.
It is interesting that the telomeric consensus sequence (TTAGGGG)n
Deletions of HS40 region has been added directly to the site of the break. Because this mutation
α -Thalassemia is stably inherited, telomeric DNA alone appears sufficient to stabilize
+
the broken chromosome end. This observation raises the possibility that
Deletions involving α or α genes
2 1 other genetic diseases result from chromosomal truncations.
Point mutations involving α or α genes Several deletions have been identified that appear to downregu-
2 1
mRNA processing late α-globin genes by removing the α-globin LCR (HS40). 7,136,137 In each
case, the α-globin genes are left intact, although in one the 3′ breakpoint
Splice site
is found between the ξ and ψξ genes, thus removing the ξ gene. These
Poly(A) signal deletions appear to completely inactivate the α-globin gene complex,
mRNA translation just as deletions of the β-globin LCR inactivate the entire β-gene com-
plex. Such deletions have not been observed in the homozygous state,
Initiation
presumably because they would be lethal.
Nonsense, frameshift
Termination
α -Thalassemia Gene Deletions
+
Posttranslational The most common forms of α -thalassemia (–α and –α ) involve
+
4.2
3.7
Unstable α-globin variants deletion of one or the other of the duplicated α-globin genes (see
α-Thalassemia Mental Retardation Figs. 48–10 and 48–11).
Each α gene is located within a region of homology approximately
ATR-16 4 kb long, interrupted by two nonhomologous regions. The homolo-
Deletions or telomeric truncations of 16p gous regions are believed to have resulted from an ancient duplication
Translocations event and to have subsequently subdivided, presumably by insertions
and deletions, to give three homologous subsegments referred to as
ATR-X X, Y, and Z (see Fig. 48–11). The duplicated Z boxes are 3.7 kb apart,
Mutations of ATR-X and the X boxes are 4.2 kb apart. Misalignment and reciprocal crossover
between these segments at meiosis can give rise to chromosomes with
Deletions
either single (–α) or triplicated (ααα) α-globin genes. Such an occur-
Splice site rence between homologous Z boxes deletes 3.7 kb of DNA (rightward
Missense deletion). A similar crossover between the two X blocks deletes 4.2 kb of
DNA (leftward deletion –α ). The corresponding triplicated α-gene
4.2 138
Nonsense
arrangements are referred to as ααα anti–3.7 and α anti–4.2 139–141 More detailed
.
note: Complete lists of individual mutations are found in Refs. 7, 10, analysis of these crossover events indicates they occur more commonly
3.7
and 51. in the Z box. At least three different –α deletions have been found,
Kaushansky_chapter 48_p0725-0758.indd 737 9/18/15 2:57 PM