Page 1010 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1010
974 Part Seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
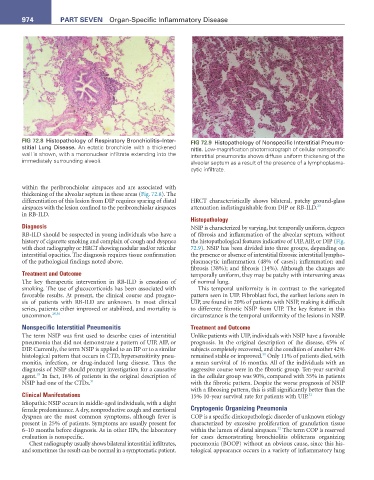
FIG 72.8 Histopathology of Respiratory Bronchiolitis–Inter- FIG 72.9 Histopathology of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumo-
stitial Lung Disease. An ectatic bronchiole with a thickened nitis. Low-magnification photomicrograph of cellular nonspecific
wall is shown, with a mononuclear infiltrate extending into the interstitial pneumonitis shows diffuse uniform thickening of the
immediately surrounding alveoli. alveolar septum as a result of the presence of a lymphoplasma-
cytic infiltrate.
within the peribronchiolar airspaces and are associated with
thickening of the alveolar septum in these areas (Fig. 72.8). The
differentiation of this lesion from DIP requires sparing of distal HRCT characteristically shows bilateral, patchy ground-glass
airspaces with the lesion confined to the peribronchiolar airspaces attenuation indistinguishable from DIP or RB-ILD. 23
in RB-ILD.
Histopathology
Diagnosis NSIP is characterized by varying, but temporally uniform, degrees
RB-ILD should be suspected in young individuals who have a of fibrosis and inflammation of the alveolar septum, without
history of cigarette smoking and complain of cough and dyspnea the histopathological features indicative of UIP, AIP, or DIP (Fig.
with chest radiography or HRCT showing nodular and/or reticular 72.9). NSIP has been divided into three groups, depending on
interstitial opacities. The diagnosis requires tissue confirmation the presence or absence of interstitial fibrosis: interstitial lympho-
of the pathological findings noted above. plasmacytic inflammation (48% of cases); inflammation and
fibrosis (38%); and fibrosis (14%). Although the changes are
Treatment and Outcome temporally uniform, they may be patchy with intervening areas
The key therapeutic intervention in RB-ILD is cessation of of normal lung.
smoking. The use of glucocorticoids has been associated with This temporal uniformity is in contrast to the variegated
favorable results. At present, the clinical course and progno- pattern seen in UIP. Fibroblast foci, the earliest lesions seen in
sis of patients with RB-ILD are unknown. In most clinical UIP, are found in 20% of patients with NSIP, making it difficult
series, patients either improved or stabilized, and mortality is to differente fibrotic NSIP from UIP. The key feature in this
uncommon. 29,30 circumstance is the temporal uniformity of the lesions in NSIP.
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonitis Treatment and Outcome
The term NSIP was first used to describe cases of interstitial Unlike patients with UIP, individuals with NSIP have a favorable
pneumonia that did not demonstrate a pattern of UIP, AIP, or prognosis. In the original description of the disease, 45% of
DIP. Currently, the term NSIP is applied to an IIP or to a similar subjects completely recovered, and the condition of another 42%
31
histological pattern that occurs in CTD, hypersensitivity pneu- remained stable or improved. Only 11% of patients died, with
monitis, infection, or drug-induced lung disease. Thus the a mean survival of 16 months. All of the individuals with an
diagnosis of NSIP should prompt investigation for a causative aggressive course were in the fibrotic group. Ten-year survival
18
agent. In fact, 16% of patients in the original description of in the cellular group was 90%, compared with 35% in patients
NSIP had one of the CTDs. 31 with the fibrotic pattern. Despite the worse prognosis of NSIP
with a fibrosing pattern, this is still significantly better than the
Clinical Manifestations 15% 10-year survival rate for patients with UIP. 32
Idiopathic NSIP occurs in middle-aged individuals, with a slight
female predominance. A dry, nonproductive cough and exertional Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia
dyspnea are the most common symptoms, although fever is COP is a specific clinicopathologic disorder of unknown etiology
present in 25% of patients. Symptoms are usually present for characterized by excessive proliferation of granulation tissue
33
6–10 months before diagnosis. As in other IIPs, the laboratory within the lumen of distal airspaces. The term COP is reserved
evaluation is nonspecific. for cases demonstrating bronchiolitis obliterans organizing
Chest radiography usually shows bilateral interstitial infiltrates, pneumonia (BOOP) without an obvious cause, since this his-
and sometimes the result can be normal in a symptomatic patient. tological appearance occurs in a variety of inflammatory lung