Page 1006 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1006
970 Part Seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
an interplay between immunological, genetic, environmental,
16
and viral factors (Fig. 72.4). Some cases of IPF are familial,
inherited as an autosomal dominant trait with variable penetrance.
Recently, dysregulated expression of a mucin gene, MUC5B, has
19
been associated with development of familial IPF. Mutations
in the telomerase ribonucleoprotein complex associated with
16
telomere shortening have also been linked with familial IPF.
In addition, surfactant protein C mutations have been rarely
associated with IPF.
In the normal lung, the interstitium is thin and delicate with
A few lymphoid cells and fibroblasts. Following the initiation of
the inflammatory process, damage to the alveolar epithelial cell
occurs, followed by vascular leak, fibroblast activation and
proliferation, ECM synthesis, and activation of the innate immune
16
system. The release of danger-associated molecular patterns
from dead or dying cells results in macrophage activation. Fol-
lowing activation, alveolar macrophages secrete IL-1, IL-8, tumor
necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), PDGF, and IGF-1. This cytokine
milieu promotes the activation and recruitment of neutrophils
and lymphocytes to the area of alveolitis.
T lymphocytes, which accumulate in the alveolar space and
interstitium, express an activated phenotype, including the
expression of human leukocyte antigen D-related (HLA-DR)
and IL-2 receptor. Following activation, CD4 T cells evolve into
three major subsets distinguished by the cytokines produced
B (Chapters 9 and 16). In IPF, T cells expressing a Th2-type
phenotype predominate, producing IL-4, -5, and -13. In addition,
the Th17 cytokine, IL-17A, has been linked to the development
of bleomycin-induced lung injury and collagen deposition. 11,12
Evidence also suggests that patients with IPF have oligoclonal
CD4 T-cell expansions that proliferate in response to antigens
20
present in diseased tissue. Treg function may be impaired in
13
patients with IPF. In addition, immune complexes have been
identified in the serum and lungs of patients with IPF. 21
In addition to their role as scavengers, alveolar macrophages
are vital in the repair phase of inflammation. However, the
distinguishing feature between a self-resolving inflammatory
process and a fibrotic response, as seen in IPF, is the accumulation
of collagen. Evidence suggests that the fibrotic process in IPF is
a consequence of dysregulation of both collagen synthesis and
degradation. Macrophage-derived growth factors, including
C
TGF-β, PDGF, and IGF-1, stimulate fibroblast proliferation and
22
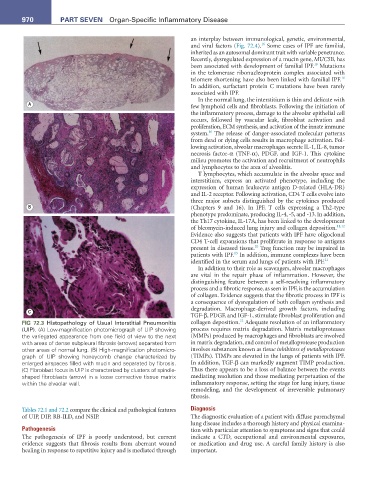
FIG 72.3 Histopathology of Usual Interstitial Pneumonitis collagen deposition. Adequate resolution of an inflammatory
(UIP). (A) Low-magnification photomicrograph of UIP showing process requires matrix degradation. Matrix metalloproteases
the variegated appearance from one field of view to the next (MMPs) produced by macrophages and fibroblasts are involved
with areas of dense subpleural fibrosis (arrows) separated from in matrix degradation, and control of metalloprotease production
other areas of normal lung. (B) High-magnification photomicro- involves substances known as tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases
graph of UIP showing honeycomb change characterized by (TIMPs). TIMPs are elevated in the lungs of patients with IPF.
enlarged airspaces filled with mucin and separated by fibrosis. In addition, TGF-β can markedly augment TIMP production.
(C) Fibroblast focus in UIP is characterized by clusters of spindle- Thus there appears to be a loss of balance between the events
shaped fibroblasts (arrow) in a loose connective tissue matrix mediating resolution and those mediating perpetuation of the
within the alveolar wall. inflammatory response, setting the stage for lung injury, tissue
remodeling, and the development of irreversible pulmonary
fibrosis.
Tables 72.1 and 72.2 compare the clinical and pathological features Diagnosis
of UIP, DIP, RB-ILD, and NSIP. The diagnostic evaluation of a patient with diffuse parenchymal
lung disease includes a thorough history and physical examina-
Pathogenesis tion with particular attention to symptoms and signs that could
The pathogenesis of IPF is poorly understood, but current indicate a CTD, occupational and environmental exposures,
evidence suggests that fibrosis results from aberrant wound or medication and drug use. A careful family history is also
healing in response to repetitive injury and is mediated through important.