Page 1007 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1007
CHaPter 72 Immunological Lung Diseases 971
TABLE 72.1 Clinical Features of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
UIP DIP rB-ILD aIP nSIP
Mean age (years) 57 42 36 49 49
Childhood No Rare No Rare Occasionally
Onset Insidious Insidious Insidious Acute Subacute, insidious
Mortality (mean survival) 68% (5–6 years) 27% (12 years) 0% 62% (1–2 months) 11% (17 months)
Response to steroids Poor Good Good Poor Good
Recovery possible No Yes Yes Yes Yes
AIP, acute interstitial pneumonitis; DIP, desquamative interstitial pneumonitis; NSIP, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; RB-ILD, respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung
disease; UIP, usual interstitial pneumonitis.
Adapted from Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathological classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: 1301.
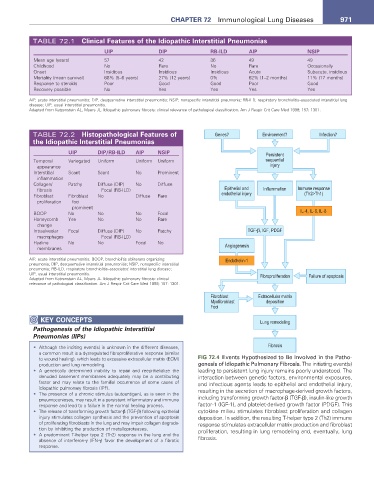
TABLE 72.2 Histopathological Features of Genes? Environment? Infection?
the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
UIP DIP/rB-ILD aIP nSIP Persistent
Temporal Variegated Uniform Uniform Uniform sequential
appearance injury
Interstitial Scant Scant No Prominent
inflammation
Collagen/ Patchy Diffuse (DIP) No Diffuse
fibrosis Focal (RB-ILD) Epithelial and Inflammation Immune response
Fibroblast Fibroblast No Diffuse Rare endothelial injury (Th2>Th1)
proliferation foci
prominent
BOOP No No No Focal IL-4, IL-6, IL-8
Honeycomb Yes No No Rare
change
Intraalveolar Focal Diffuse (DIP) No Patchy TGF-β, IGF, PDGF
macrophages Focal (RB-ILD)
Hyaline No No Focal No Angiogenesis
membranes
AIP, acute interstitial pneumonitis; BOOP, bronchiolitis obliterans organizing Endothelin-1
pneumonia; DIP, desquamative interstitial pneumonitis; NSIP, nonspecific interstitial
pneumonia; RB-ILD, respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease;
UIP, usual interstitial pneumonitis. Fibroproliferation Failure of apoptosis
Adapted from Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical
relevance of pathological classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: 1301.
Fibroblast Extracellular matrix
Myofibroblast deposition
Foci
KeY COnCePtS Lung remodeling
Pathogenesis of the Idiopathic Interstitial
Pneumonias (IIPs)
• Although the inciting event(s) is unknown in the different diseases, Fibrosis
a common result is a dysregulated fibroproliferative response (similar
to wound healing), which leads to excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) FIG 72.4 Events Hypothesized to Be Involved in the Patho-
production and lung remodeling. genesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. The initiating event(s)
• A genetically determined inability to repair and reepithelialize the leading to persistent lung injury remains poorly understood. The
denuded basement membranes adequately may be a contributing interaction between genetic factors, environmental exposures,
factor and may relate to the familial occurrence of some cases of and infectious agents leads to epithelial and endothelial injury,
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). resulting in the secretion of macrophage-derived growth factors,
• The presence of a chronic stimulus (autoantigen), as is seen in the
pneumoconioses, may result in a persistent inflammatory and immune including transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), insulin-like growth
response and lead to a failure in the normal healing process. factor-1 (IGF-1), and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). This
• The release of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) following epithelial cytokine milieu stimulates fibroblast proliferation and collagen
injury stimulates collagen synthesis and the prevention of apoptosis deposition. In addition, the resulting T-helper type 2 (Th2) immune
of proliferating fibroblasts in the lung and may impair collagen degrada- response stimulates extracellular matrix production and fibroblast
tion by inhibiting the production of metalloproteases. proliferation, resulting in lung remodeling and, eventually, lung
• A predominant T-helper type 2 (Th2) response in the lung and the fibrosis.
absence of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) favor the development of a fibrotic
response.