Page 114 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 114
98 Part one Principles of Immune Response
correct class II folding. CLIP occupies the peptide-binding pocket
of the class II molecule. This prevents premature occupation of
the peptide-binding pocket by self peptides, and it ensures the
CD4T cell conformation integrity of the membrane distal, class II peptide
binding domains. Successful assembly of invariant chain with
MHC class II allows egress of the complex from the ER to later
biosynthetic compartments. In this context, invariant chain acts
Golgi as a molecular chaperone.
As they leave the ER, MHC class II and invariant chain are
cotranslationally modified by the addition of complex carbohy-
drates into the Golgi complex. Either directly from the trans-Golgi
network or after a short-lived cell-surface intermediate, they are
Endoplasmic then selectively sorted into the endosomal compartment of APCs.
reticulum
The amino terminal cytosolic tail of invariant chain plays a key
Intact Invariant MHC class II HLA-DM HLA-DO role in the sorting event, which is mediated by the adaptor protein
antigen chain α and β AP-2. Once in the endosomal compartments, invariant chain is
degraded by defined sequential proteolytic events mediated by
Endosomal Clip fragment Antigenic MHC class II pH-dependent proteases, including aspartyl and cysteine proteases.
proteases of Invariant chain peptide peptide complexes The key proteases that cleaves invariant at CLIP’s amino-terminus
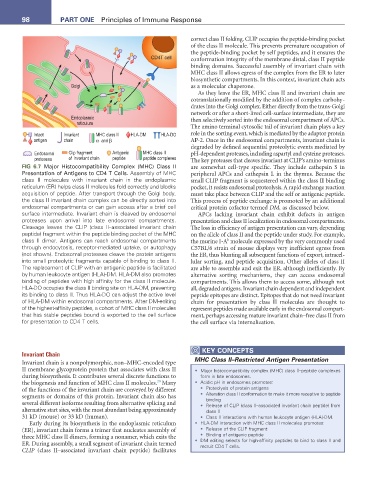
FIG 6.7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class II are somewhat cell-type specific. They include cathepsin S in
Presentation of Antigens to CD4 T Cells. Assembly of MHC peripheral APCs and cathepsin L in the thymus. Because the
class II molecules with invariant chain in the endoplasmic small CLIP fragment is sequestered within the class II binding
reticulum (ER) helps class II molecules fold correctly and blocks pocket, it resists endosomal proteolysis. A rapid exchange reaction
acquisition of peptide. After transport through the Golgi body, must take place between CLIP and the self or antigenic peptide.
the class II invariant chain complex can be directly sorted into This process of peptide exchange is promoted by an additional
endosomal compartments or can gain access after a brief cell critical protein cofactor termed DM, as discussed below.
surface intermediate. Invariant chain is cleaved by endosomal APCs lacking invariant chain exhibit defects in antigen
proteases upon arrival into late endosomal compartments. presentation and class II localization in endosomal compartments.
Cleavage leaves the CLIP (class II–associated invariant chain The loss in efficiency of antigen presentation can vary, depending
peptide) fragment within the peptide binding pocket of the MHC on the allele of class II and the peptide under study. For example,
class II dimer. Antigens can reach endosomal compartments the murine I-A molecule expressed by the very commonly used
b
through endocytosis, receptor-mediated uptake, or autophagy C57BL/6 strain of mouse displays very inefficient egress from
(not shown). Endosomal proteases cleave the protein antigens the ER, thus blunting all subsequent functions of export, intracel-
into small proteolytic fragments capable of binding to class II. lular sorting, and peptide acquisition. Other alleles of class II
The replacement of CLIP with an antigenic peptide is facilitated are able to assemble and exit the ER, although inefficiently. By
by human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DM. HLA-DM also promotes alternative sorting mechanisms, they can access endosomal
binding of peptides with high affinity for the class II molecule. compartments. This allows them to access some, although not
HLA-DO occupies the class II binding site on HLA-DM, preventing all, degraded antigens. Invariant chain dependent and independent
its binding to class II. Thus HLA-DO can adjust the active level peptide epitopes are distinct. Epitopes that do not need invariant
of HLA-DM within endosomal compartments. After DM-editing chain for presentation by class II molecules are thought to
of the highest-affinity peptides, a cohort of MHC class II molecules represent peptides made available early in the endosomal compart-
that has stable peptides bound is exported to the cell surface ment, perhaps accessing mature invariant chain–free class II from
for presentation to CD4 T cells. the cell surface via internalization.
KeY ConCePtS
Invariant Chain
Invariant chain is a nonpolymorphic, non–MHC-encoded type MHC Class II–Restricted Antigen Presentation
II membrane glycoprotein protein that associates with class II • Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II–peptide complexes
during biosynthesis. It contributes several discrete functions to form in late endosomes.
20
the biogenesis and function of MHC class II molecules. Many • Acidic pH in endosomes promotes:
of the functions of the invariant chain are conveyed by different • Proteolysis of protein antigens
segments or domains of this protein. Invariant chain also has • Alteration class II conformation to make it more receptive to peptide
binding
several different isoforms resulting from alternative splicing and • Release of CLIP (class II–associated invariant chain peptide) from
alternative start sites, with the most abundant being approximately class II
31 kD (mouse) or 33 kD (human). • Class II interactions with human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DM.
Early during its biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum • HLA-DM interaction with MHC class II molecules promotes:
(ER), invariant chain forms a trimer that nucleates assembly of • Release of the CLIP fragment
three MHC class II dimers, forming a nonamer, which exits the • Binding of antigenic peptide
ER. During assembly, a small segment of invariant chain termed • DM editing selects for high-affinity peptides to bind to class II and
recruit CD4 T cells.
CLIP (class II–associated invariant chain peptide) facilitates