Page 1287 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1287
CHaPtEr 92 Flow Cytometry 1249
600 1000 10 4
G1
800 10 3
400
600 Late
# Cells SSC Live PI 10 2 Early
200 400
S G2-M 1
200 10
Live
Dead
0 0 10 0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 0 200 400 600 800 1000 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
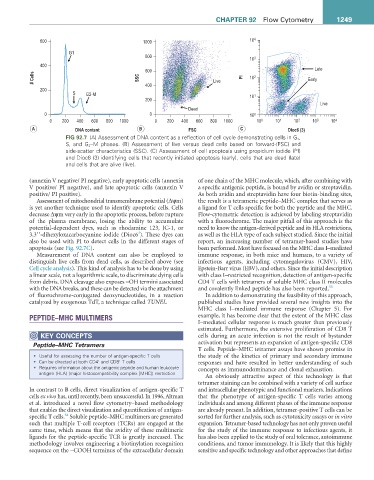
A DNA content B FSC C Dioc6 (3)
FIG 92.7 (A) Assessment of DNA content as a reflection of cell cycle demonstrating cells in G 1 ,
S, and G 2 –M phases. (B) Assessment of live versus dead cells based on forward-(FSC) and
side-scatter characteristics (SSC). (C) Assessment of cell apoptosis using propidium iodide (PI)
and Dioc6 (3) identifying cells that recently initiated apoptosis (early), cells that are dead (late)
and cells that are alive (live).
(annexin V negative/ PI negative), early apoptotic cells (annexin of one chain of the MHC molecule, which, after combining with
V positive/ PI negative), and late apoptotic cells (annexin V a specific antigenic peptide, is bound by avidin or streptavidin.
positive/ PI positive). As both avidin and streptavidin have four biotin-binding sites,
Assessment of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Δψm) the result is a tetrameric peptide–MHC complex that serves as
is yet another technique used to identify apoptotic cells. Cells a ligand for T cells specific for both the peptide and the MHC.
decrease Δψm very early in the apoptotic process, before rupture Flow-cytometric detection is achieved by labeling streptavidin
of the plasma membrane, losing the ability to accumulate with a fluorochrome. The major pitfall of this approach is the
potential-dependent dyes, such as rhodamine 123, JC-1, or need to know the antigen-derived peptide and its HLA restrictions,
3
3,3’ ’-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide (Dioc6 ). These dyes can as well as the HLA type of each subject studied. Since the initial
also be used with PI to detect cells in the different stages of report, an increasing number of tetramer-based studies have
apoptosis (see Fig. 92.7C). been performed. Most have focused on the MHC class I–mediated
Measurement of DNA content can also be employed to immune response, in both mice and humans, to a variety of
distinguish live cells from dead cells, as described above (see infectious agents, including cytomegalovirus (CMV), HIV,
Cell cycle analysis). This kind of analysis has to be done by using Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and others. Since the initial description
a linear scale, not a logarithmic scale, to discriminate dying cells with class I–restricted recognition, detection of antigen-specific
from debris. DNA cleavage also exposes −OH termini associated CD4 T cells with tetramers of soluble MHC class II molecules
with the DNA breaks, and these can be detected via the attachment and covalently linked peptide has also been reported. 55
of fluorochrome-conjugated deoxynucleotides, in a reaction In addition to demonstrating the feasibility of this approach,
catalyzed by exogenous TdT, a technique called TUNEL. published studies have provided several new insights into the
MHC class I–mediated immune response (Chapter 5). For
PEPTIDE–MHC MULTIMERS example, it has become clear that the extent of the MHC class
I–mediated cellular response is much greater than previously
estimated. Furthermore, the extensive proliferation of CD8 T
KEY COnCEPtS cells during an acute infection is not the result of bystander
Peptide–MHC Tetramers activation but represents an expansion of antigen-specific CD8
T cells. Peptide–MHC tetramer assays have shown promise in
• Useful for assessing the number of antigen-specific T cells the study of the kinetics of primary and secondary immune
+
+
• Can be directed at both CD4 and CD8 T cells responses and have resulted in better understanding of such
• Requires information about the antigenic peptide and human leukocyte concepts as immunodominance and clonal exhaustion.
antigen (HLA) (major histocompatibility complex [MHC]) restriction
An obviously attractive aspect of this technology is that
tetramer staining can be combined with a variety of cell surface
In contrast to B cells, direct visualization of antigen-specific T and intracellular phenotypic and functional markers. Indications
cells ex vivo has, until recently, been unsuccessful. In 1996, Altman that the phenotype of antigen-specific T cells varies among
et al. introduced a novel flow cytometry–based methodology individuals and among different phases of the immune response
that enables the direct visualization and quantification of antigen- are already present. In addition, tetramer-positive T cells can be
54
specific T cells. Soluble peptide–MHC multimers are generated sorted for further analysis, such as cytotoxicity assays or in vitro
such that multiple T-cell receptors (TCRs) are engaged at the expansion. Tetramer-based technology has not only proven useful
same time, which means that the avidity of these multimeric for the study of the immune response to infectious agents, it
ligands for the peptide-specific TCR is greatly increased. The has also been applied to the study of oral tolerance, autoimmune
methodology involves engineering a biotinylation recognition conditions, and tumor immunology. It is likely that this highly
sequence on the −COOH terminus of the extracellular domain sensitive and specific technology and other approaches that define