Page 1293 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1293
CHaPter 93 Assessment of Functional Immune Responses in Lymphocytes 1255
increased oxidative phosphorylation. T-helper cell-1 (Th1), Th2, +HDOWK\ FRQWURO
and Th17 CD4 effector T cells use glycolytic metabolism, whereas
regulatory T-cell and memory T-cell development is enhanced &' /
by fatty acid oxidation and catabolic metabolism. In particular,
memory T cells are quiescent and mainly use oxidative phos- &RXQW &RXQW &' XOJ
phorylation; however, on antigenic rechallenge, the use of oxidative
6
phosphorylation and glycolysis is rapidly facilitated. While naïve
T-cell activation and differentiation into effector cells is essential
for a normal immune response during exposure to acute antigenic
challenge, chronic antigenic stimulation via persistent antigen
exposure and/or inflammation causes an alteration of memory 3DWLHQW
T-cell differentiation, resulting in a state of T-cell exhaustion.
During T-cell exhaustion there is a progressive diminution of
effector functions, along with upregulation of several inhibitory &' /
receptors, metabolic changes, and a failure to transition to a &RXQW &RXQW &' XOJ
quiescent state and to obtain antigen-independent memory T-cell
homeostatic response. Exhausted T cells have only a limited
ability to clear pathogens or tumors; however, there is some
evidence that this is a reversible phenomenon, at least at a global
level. 7
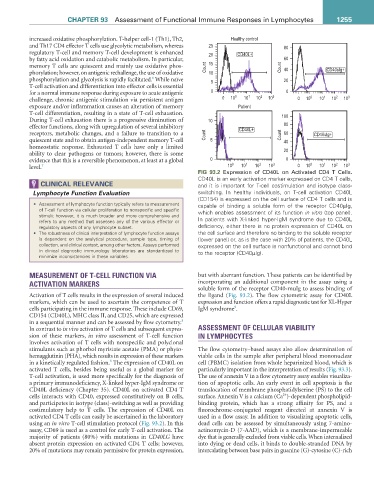
FIG 93.2 Expression of CD40L on Activated CD4 T Cells.
CD40L is an early activation marker expressed on CD4 T cells,
ClInICal relevanCe and it is important for T-cell costimulation and isotype class-
Lymphocyte Function Evaluation switching. In healthy individuals, on T-cell activation CD40L
(CD154) is expressed on the cell surface of CD4 T cells and is
• Assessment of lymphocyte function typically refers to measurement capable of binding a soluble form of the receptor CD40µIg,
of T-cell function via cellular proliferation to nonspecific and specific which enables assessment of its function in vitro (top panel).
stimuli; however, it is much broader and more comprehensive and In patients with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome due to CD40L
refers to any method that assesses any of the various effector or
regulatory aspects of any lymphocyte subset. deficiency, either there is no protein expression of CD40L on
• The robustness of clinical interpretation of lymphocyte function assays the cell surface and therefore no binding to the soluble receptor
is dependent on the analytical procedure, sample type, timing of (lower panel) or, as is the case with 20% of patients, the CD40L
collection, and clinical context, among other factors. Assays performed expressed on the cell surface is nonfunctional and cannot bind
in clinical diagnostic immunology laboratories are standardized to to the receptor (CD40µIg).
minimize inconsistencies in these variables.
MEASUREMENT OF T-CELL FUNCTION VIA but with aberrant function. These patients can be identified by
ACTIVATION MARKERS incorporating an additional component in the assay using a
soluble form of the receptor CD40-muIg to assess binding of
Activation of T cells results in the expression of several induced the ligand (Fig. 93.2). The flow cytometric assay for CD40L
markers, which can be used to ascertain the competence of T expression and function offers a rapid diagnostic test for XL-Hyper
9
cells participating in the immune response. These include CD69, IgM syndrome .
CD154 (CD40L), MHC class II, and CD25, which are expressed
8
in a sequential manner and can be assessed by flow cytometry.
In contrast to in vivo activation of T cells and subsequent expres- ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR VIABILITY
sion of these markers, in vitro assessment of T-cell function IN LYMPHOCYTES
involves activation of T cells with nonspecific and polyclonal
stimulants such as phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) or phyto- The flow cytometry–based assays also allow determination of
hemagglutinin (PHA), which results in expression of these markers viable cells in the sample after peripheral blood mononuclear
8
in a kinetically regulated fashion. The expression of CD40L on cell (PBMC) isolation from whole heparinized blood, which is
activated T cells, besides being useful as a global marker for particularly important in the interpretation of results (Fig. 93.3).
T-cell activation, is used more specifically for the diagnosis of The use of annexin V in a flow cytometry assay enables visualiza-
a primary immunodeficiency, X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome or tion of apoptotic cells. An early event in cell apoptosis is the
CD40L deficiency (Chapter 35). CD40L on activated CD4 T translocation of membrane phosphatidylserine (PS) to the cell
2+
cells interacts with CD40, expressed constitutively on B cells, surface. Annexin V is a calcium (Ca )-dependent phospholipid-
and participates in isotype (class)-switching as well as providing binding protein, which has a strong affinity for PS, and a
costimulatory help to T cells. The expression of CD40L on fluorochrome-conjugated reagent directed at annexin V is
activated CD4 T cells can easily be ascertained in the laboratory used in a flow assay. In addition to visualizing apoptotic cells,
using an in vitro T-cell stimulation protocol (Fig. 93.2). In this dead cells can be assessed by simultaneously using 7-amino-
assay, CD69 is used as a control for early T-cell activation. The actinomycin-D (7-AAD), which is a membrane-impermeable
majority of patients (80%) with mutations in CD40LG have dye that is generally excluded from viable cells. When internalized
absent protein expression on activated CD4 T cells; however, into dying or dead cells, it binds to double-stranded DNA by
20% of mutations may remain permissive for protein expression, intercalating between base pairs in guanine (G)-cytosine (C)-rich