Page 1294 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1294
1256 Part eleven Diagnostic Immunology
10 3 KeY COnCePtS
Annexin V+7-AAD+
T-Cell Activation and Function
• Cognate recognition of peptide major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
10 2 complex on the APC by the T-cell receptor results in formation of the
immunological synapse.
• Activated T cells express early activation markers, such as CD69 and
CD40L. Other T-cell activation markers include CD25 and MHC class
10 1 II (human leukocyte antigen–D related [HLA-DR]).
• T cells can be stimulated to proliferate using nonspecific stimulants
such as plant lectins (mitogens) and cross-linking of the CD3 coreceptor,
along with other costimulatory molecules (e.g., anti-CD28) or in the
2 presence of exogenous interleukin-2 (IL-2).
• The magnitude of antigen-specific T-cell proliferation is dependent on
the starting frequency of antigen-specific T cells.
0 • Flow cytometry–based assays of T-cell proliferation offer the advantages
of high resolution, accounting for cellular dilution due to T-cell lym-
–2 phopenia and single-cell analysis.
Viable cells Annexin V+
0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3
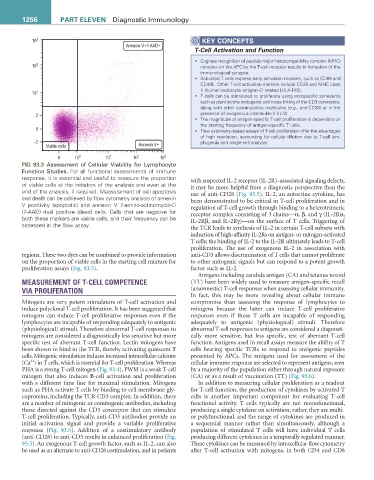
FIG 93.3 Assessment of Cellular Viability for Lymphocyte
Function Studies. For all functional assessments of immune
response, it is essential and useful to measure the proportion with suspected IL-2 receptor (IL-2R)–associated signaling defects,
of viable cells at the initiation of the analysis and even at the it may be more helpful from a diagnostic perspective than the
end of the analysis, if required. Measurement of cell apoptosis use of anti-CD28 (Fig. 93.5). IL-2, an autocrine cytokine, has
and death can be achieved by flow cytometry analysis of annexin been demonstrated to be critical in T-cell proliferation and in
V positivity (apoptotic) and annexin V 7-amino-actinomycin-D regulation of T-cell growth through binding to a heterotrimeric
(7-AAD) dual positive (dead) cells. Cells that are negative for receptor complex consisting of 3 chains—α, β, and γ (IL-2Rα,
both these markers are viable cells, and their frequency can be IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ)—on the surface of T cells. Triggering of
assessed in the flow assay. the TCR leads to synthesis of IL-2 in certain T-cell subsets with
induction of high-affinity IL-2Rs on antigen- or mitogen-activated
T cells; the binding of IL-2 to the IL-2R ultimately leads to T-cell
proliferation. The use of exogenous IL-2 in association with
regions. These two dyes can be combined to provide information anti-CD3 allows discrimination of T cells that cannot proliferate
on the proportion of viable cells in the starting cell mixture for to other mitogenic signals but can respond to a potent growth
proliferation assays (Fig. 93.3). factor such as IL-2.
Antigens including candida antigen (CA) and tetanus toxoid
MEASUREMENT OF T-CELL COMPETENCE (TT) have been widely used to measure antigen-specific recall
VIA PROLIFERATION (anamnestic) T-cell responses when assessing cellular immunity.
In fact, this may be more revealing about cellular immune
Mitogens are very potent stimulators of T-cell activation and compromise than assessing the response of lymphocytes to
induce polyclonal T-cell proliferation. It has been suggested that mitogens because the latter can induce T-cell proliferative
mitogens can induce T-cell proliferative responses even if the responses even if those T cells are incapable of responding
lymphocytes are incapable of responding adequately to antigenic adequately to antigenic (physiological) stimuli. Therefore
(physiological) stimuli. Therefore abnormal T-cell responses to abnormal T-cell responses to antigens are considered a diagnosti-
mitogens are considered a diagnostically less sensitive but more cally more sensitive, but less specific, test of aberrant T-cell
specific test of aberrant T-cell function. Lectin mitogens have function. Antigens used in recall assays measure the ability of T
been shown to bind to the TCR, thereby activating quiescent T cells bearing specific TCRs to respond to antigenic peptides
cells. Mitogenic stimulation induces increased intracellular calcium presented by APCs. The antigens used for assessment of the
2+
(Ca ) in T cells, which is essential for T-cell proliferation. Whereas cellular immune response are selected to represent antigens, seen
PHA is a strong T-cell mitogen (Fig. 93.4), PWM is a weak T-cell by a majority of the population either through natural exposure
mitogen that also induces B-cell activation and proliferation (CA) or as a result of vaccination (TT) (Fig. 93.6).
with a different time line for maximal stimulation. Mitogens In addition to measuring cellular proliferation as a readout
such as PHA activate T cells by binding to cell membrane gly- for T-cell function, the production of cytokines by activated T
coproteins, including the TCR-CD3 complex. In addition, there cells is another important component for evaluating T-cell
are a number of mitogenic or comitogenic antibodies, including functional activity. T cells typically are not monofunctional,
those directed against the CD3 coreceptor that can stimulate producing a single cytokine on activation; rather, they are multi-
T-cell proliferation. Typically, anti-CD3 antibodies provide an or polyfunctional, and the range of cytokines are produced in
initial activation signal and provide a variable proliferative a sequential manner rather than simultaneously, although a
response (Fig. 93.5). Addition of a costimulatory antibody population of stimulated T cells will have individual T cells
(anti-CD28) to anti-CD3 results in enhanced proliferation (Fig. producing different cytokines in a temporally regulated manner.
93.5). An exogenous T-cell growth factor, such as IL-2, can also These cytokines can be measured by intracellular flow cytometry
be used as an alternate to anti-CD28 costimulation, and in patients after T-cell activation with mitogens, in both CD4 and CD8