Page 1296 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1296
1258 Part eleven Diagnostic Immunology
Healthy donor PHA/CD45 PHA/CD3
80
60
60 Proliferating CD45+ lymphs Proliferating CD3+ T cells
Count 40 Count 40
20
20
0 0
0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3
Fluorescence Fluorescence
Patient with T cell lymphopenia
PHA/CD45 PHA/CD3
150
30
100 Proliferating CD45+ lymphs Proliferating CD3+ T cells
Count Count 20
50
10
0 0
0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3
Fluorescence Fluorescence
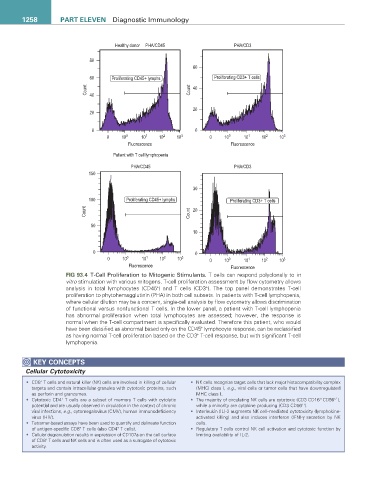
FIG 93.4 T-Cell Proliferation to Mitogenic Stimulants. T cells can respond polyclonally to in
vitro stimulation with various mitogens. T-cell proliferation assessment by flow cytometry allows
+
+
analysis in total lymphocytes (CD45 ) and T cells (CD3 ). The top panel demonstrates T-cell
proliferation to phytohemagglutinin (PHA) in both cell subsets. In patients with T-cell lymphopenia,
where cellular dilution may be a concern, single-cell analysis by flow cytometry allows discrimination
of functional versus nonfunctional T cells. In the lower panel, a patient with T-cell lymphopenia
has abnormal proliferation when total lymphocytes are assessed; however, the response is
normal when the T-cell compartment is specifically evaluated. Therefore this patient, who would
+
have been classified as abnormal based only on the CD45 lymphocyte response, can be reclassified
+
as having normal T-cell proliferation based on the CD3 T-cell response, but with significant T-cell
lymphopenia.
KeY COnCePtS
Cellular Cytotoxicity
• CD8 T cells and natural killer (NK) cells are involved in killing of cellular • NK cells recognize target cells that lack major histocompatibility complex
+
targets and contain intracellular granules with cytotoxic proteins, such (MHC) class I, e.g., viral cells or tumor cells that have downregulated
as perforin and granzymes. MHC class I.
+/−
+
++
• Cytotoxic CD4 T cells are a subset of memory T cells with cytolytic • The majority of circulating NK cells are cytotoxic (CD3 CD16 CD56 ),
−
++
−
potential and are usually observed in circulation in the context of chronic while a minority are cytokine producing (CD3 CD56 ).
viral infections, e.g., cytomegalovirus (CMV), human immunodeficiency • Interleukin (IL)-2 augments NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity (lymphokine-
virus (HIV). activated killing) and also induces interferon (IFN)-γ secretion by NK
• Tetramer-based assays have been used to quantify and delineate function cells.
of antigen-specific CD8 T cells (also CD4 T cells). • Regulatory T cells control NK cell activation and cytotoxic function by
+
+
• Cellular degranulation results in expression of CD107a on the cell surface limiting availability of IL-2.
+
of CD8 T cells and NK cells and is often used as a surrogate of cytotoxic
activity.