Page 1298 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1298
1260 Part eleven Diagnostic Immunology
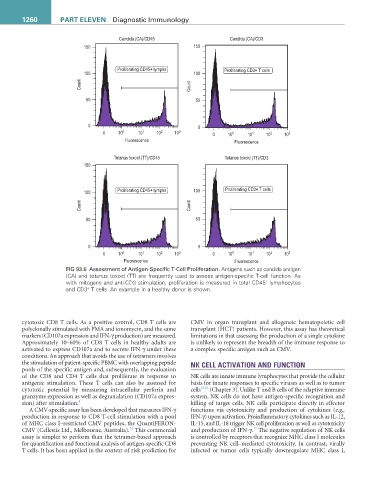
&DQGLGD &$ &' &DQGLGD &$ &'
3UROLIHUDWLQJ &' O\PSKV 3UROLIHUDWLQJ &' 7 FHOOV
&RXQW &RXQW
)OXRUHVFHQFH )OXRUHVFHQFH
7HWDQXV WR[RLG 77 &' 7HWDQXV WR[RLG 77 &'
3UROLIHUDWLQJ &' O\PSKV 3UROLIHUDWLQJ &' 7 FHOOV
&RXQW &RXQW
)OXRUHVFHQFH )OXRUHVFHQFH
FIG 93.6 Assessment of Antigen-Specific T-Cell Proliferation. Antigens such as candida antigen
(CA) and tetanus toxoid (TT) are frequently used to assess antigen-specific T-cell function. As
+
with mitogens and anti-CD3 stimulation, proliferation is measured in total CD45 lymphocytes
+
and CD3 T cells. An example in a healthy donor is shown.
cytotoxic CD8 T cells. As a positive control, CD8 T cells are CMV in organ transplant and allogeneic hematopoietic cell
polyclonally stimulated with PMA and ionomycin, and the same transplant (HCT) patients. However, this assay has theoretical
markers (CD107a expression and IFN-γ production) are measured. limitations in that assessing the production of a single cytokine
Approximately 10–60% of CD8 T cells in healthy adults are is unlikely to represent the breadth of the immune response to
activated to express CD107a and to secrete IFN-γ under these a complex specific antigen such as CMV.
conditions. An approach that avoids the use of tetramers involves
the stimulation of patient-specific PBMC with overlapping peptide NK CELL ACTIVATION AND FUNCTION
pools of the specific antigen and, subsequently, the evaluation
of the CD8 and CD4 T cells that proliferate in response to NK cells are innate immune lymphocytes that provide the cellular
antigenic stimulation. These T cells can also be assessed for basis for innate responses to specific viruses as well as to tumor
cytotoxic potential by measuring intracellular perforin and cells 15,16 (Chapter 3). Unlike T and B cells of the adaptive immune
granzyme expression as well as degranulation (CD107a expres- system, NK cells do not have antigen-specific recognition and
sion) after stimulation. 8 killing of target cells. NK cells participate directly in effector
A CMV-specific assay has been developed that measures IFN-γ functions via cytotoxicity and production of cytokines (e.g.,
production in response to CD8 T-cell stimulation with a pool IFN-γ) upon activation. Proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-12,
of MHC class I–restricted CMV peptides, the QuantiFERON- IL-15, and IL-18 trigger NK cell proliferation as well as cytotoxicity
14
17
CMV (Cellestis Ltd., Melbourne, Australia). This commercial and production of IFN-γ. The negative regulation of NK cells
assay is simpler to perform than the tetramer-based approach is controlled by receptors that recognize MHC class I molecules
for quantification and functional analysis of antigen-specific CD8 preventing NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity. In contrast, virally
T cells. It has been applied in the context of risk prediction for infected or tumor cells typically downregulate MHC class I,