Page 1299 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1299
CHaPter 93 Assessment of Functional Immune Responses in Lymphocytes 1261
making them appropriate targets of NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity [neural cell adhesion molecule]) and CD16 (FcγRIII). NK cells
in the presence of relevant ligands expressed by the target cell. can be subdivided into two major subsets based on their relative
18
NK cells, like cytotoxic T cells, contain granules with cytotoxic expression of CD56 and CD16: CD16 +++(bright) CD56 +/−(dim) NK
proteins including perforin and granzymes, which are serine cells, referred to as cytotoxic NK cells, and CD56 +++(bright) CD16
+/−
proteases that recognize different substrates. or CD16 NK cells, known as regulatory or cytokine-producing
NK cells (Fig. 93.8). The majority (~90%) of circulating human
NK CELL CYTOTOXICITY NK cells belong to the cytotoxic category, while a minority (10%)
represent cytokine-producing NK cells. Cytotoxicity can be
The majority of NK cells can be identified by a lack of CD3 on the subdivided into natural or spontaneous cytotoxicity directed
cell surface in conjunction with the expression of CD56 (NCAM largely toward virally infected cells or tumor cells, in the absence
66& $ &'
+/$ DOOHOH &09 SHSWLGH
$ SS
&' &' $ SS
% SS
+/$ $ WHWUDPHU +/$ % WHWUDPHU % ,(
% SS
5HOHYHQW WHWUDPHU 5HOHYHQW WHWUDPHU
&' &'
$
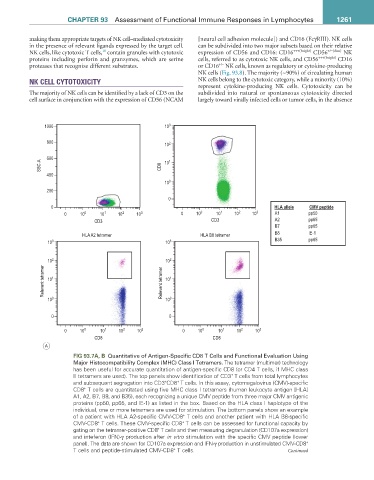
FIG 93.7a, B Quantitative of Antigen-Specific CD8 T Cells and Functional Evaluation Using
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I Tetramers. The tetramer (multimer) technology
has been useful for accurate quantitation of antigen-specific CD8 (or CD4 T cells, if MHC class
II tetramers are used). The top panels show identification of CD3 T cells from total lymphocytes
+
and subsequent segregation into CD3 CD8 T cells. In this assay, cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific
+
+
+
CD8 T cells are quantitated using five MHC class I tetramers (human leukocyte antigen [HLA]
A1, A2, B7, B8, and B35), each recognizing a unique CMV peptide from three major CMV antigenic
proteins (pp50, pp65, and IE-1) as listed in the box. Based on the HLA class I haplotype of the
individual, one or more tetramers are used for stimulation. The bottom panels show an example
+
of a patient with HLA A2-specific CMV-CD8 T cells and another patient with HLA B8-specific
+
CMV-CD8 T cells. These CMV-specific CD8 T cells can be assessed for functional capacity by
+
gating on the tetramer-positive CD8 T cells and then measuring degranulation (CD107a expression)
+
and inteferon (IFN)-γ production after in vitro stimulation with the specific CMV peptide (lower
+
panel). The data are shown for CD107a expression and IFN-γ production in unstimulated CMV-CD8
+
T cells and peptide-stimulated CMV-CD8 T cells. Continued