Page 1355 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1355
APPENDIX 1 Selected CD Molecules and Their Characteristics 1315
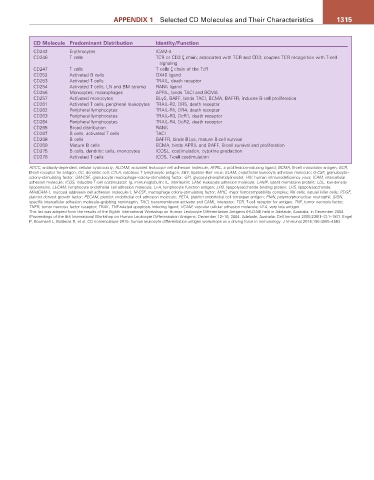
CD Molecule Predominant Distribution Identity/Function
CD242 Erythrocytes ICAM-4
CD246 T cells TCR or CD3 ζ chain; associated with TCR and CD3; couples TCR recognition with T-cell
signaling
CD247 T cells T cells ζ chain of the TcR
CD252 Activated B cells OX40 ligand
CD253 Activated T cells TRAIL, death receptor
CD254 Activated T cells, LN and BM stroma RANK ligand
CD256 Monocytes, macrophages APRIL, binds TACI and BCMA
CD257 Activated monocytes BLyS, BAFF, binds TACI, BCMA, BAFFR, induces B-cell proliferation
CD261 Activated T cells, peripheral leukocytes TRAIL-R2, DR5, death receptor
CD262 Peripheral lymphocytes TRAIL-R1, DR4, death receptor
CD263 Peripheral lymphocytes TRAIL-R3, DcR1, death receptor
CD264 Peripheral lymphocytes TRAIL-R4, DcR2, death receptor
CD265 Broad distribution RANK
CD267 B cells, activated T cells TACI
CD268 B cells BAFFR, binds BLys, mature B-cell survival
CD269 Mature B cells BCMA, binds APRIL and BAFF, B-cell survival and proliferation
CD275 B cells, dendritic cells, monocytes ICOSL, costimulation, cytokine production
CD278 Activated T cells ICOS, T-cell costimulation
ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; ALCAM, activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule; APRIL, a proliferation-inducing ligand; BCMA, B-cell maturation antigen; BCR,
B-cell receptor for antigen; DC, dendritic cell; CTLA, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; ELAM, endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule; G-CSF, granulocyte–
colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage–colony-stimulating factor; GPI, glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ICAM, intercellular
adhesion molecule; ICOS, inducible T-cell costimulator; Ig, immunoglobulin; IL, interleukin; LAM, leukocyte adhesion molecule; LAMP, latent membrane protein; LDL, low-density
lipoproteins; LECAM, lymphocyte endothelial cell adhesion molecule; LFA, lymphocyte function antigen; LPB, lipopolysaccharide binding protein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide;
MAdCAM-1, mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NK cells, natural killer cells; PDGF,
platelet-derived growth factor; PECAM, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule; PETA, platelet-endothelial cell tetraspan antigen; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophil; SIGN,
specific intercellular adhesion molecule–grabbing nonintegrin; TACI, transmembrane activator and CAML interactor; TCR, T-cell receptor for antigen; TNF, tumor necrosis factor;
TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand; VCAM, vascular cellular adhesion molecule; VLA, very late antigen.
This list was adapted from the results of the Eighth International Workshop on Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens (HLDA8) held in Adelaide, Australia, in December 2004
(Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens. December 12–16, 2004. Adelaide, Australia. Cell Immunol 2005;236[1–2]:1–187). Engel
P, Boumsell L, Balderas R, et al. CD nomenclature 2015: human leukocyte differentiation antigen workshops as a driving force in immunology. J Immunol 2015;195:4555–4563.