Page 221 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 221
200 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
No DAMP release DAMP release
Apoptosis Necroptosis Ferroptosis Mitochondria-mediated necrosis Pyroptosis
Cell death pathway Parthanatos MPT-RN
IL-1β
IL-33 Lipid peroxidation IL-18
Proinflammatory potency (in vitro only) Local inflammation Inflammation by uncontrolled DAMP release inflammation
Neglectable
Systemic
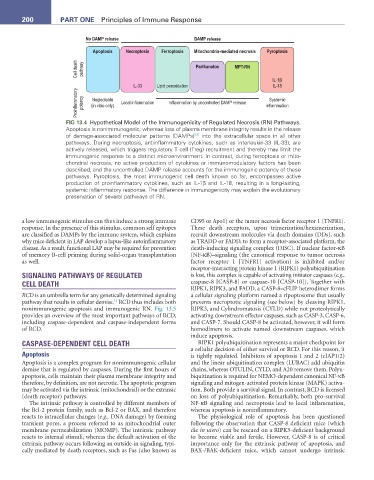
FIG 13.4 Hypothetical Model of the Immunogenicity of Regulated Necrosis (RN) Pathways.
Apoptosis is nonimmunogenic, whereas loss of plasma membrane integrity results in the release
5,6
of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) into the extracellular space in all other
pathways. During necroptosis, antiinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-33 (IL-33), are
actively released, which triggers regulatory T cell (Treg) recruitment and thereby may limit the
immunogenic response to a distinct microenvironment. In contrast, during ferroptosis or mito-
chondrial necrosis, no active production of cytokines or immunomodulatory factors has been
described, and the uncontrolled DAMP release accounts for the immunogenic potency of these
pathways. Pyroptosis, the most immunogenic cell death known so far, encompasses active
production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-18, resulting in a long-lasting,
systemic inflammatory response. The difference in immunogenicity may explain the evolutionary
preservation of several pathways of RN.
a low immunogenic stimulus can thus induce a strong immune CD95 or Apo1) or the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1).
response. In the presence of this stimulus, common self epitopes These death receptors, upon trimerization/hexamerization,
are classified as DAMPs by the immune system, which explains recruit downstream molecules via death domains (DDs), such
why mice deficient in LAP develop a lupus-like autoinflammatory as TRADD or FADD, to form a receptor-associated platform, the
disease. As a result, functional LAP may be required for prevention death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). If nuclear factor-κB
of memory B-cell priming during solid-organ transplantation (NF-κB)–signaling (the canonical response to tumor necrosis
as well. factor receptor 1 [TNFR1] activation) is inhibited and/or
receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) polyubiquitination
SIGNALING PATHWAYS OF REGULATED is lost, this complex is capable of activating initiator caspases (e.g.,
CELL DEATH caspase-8 [CASP-8] or caspase-10 [CASP-10]). Together with
RIPK1, RIPK3, and FADD, a CASP-8–cFLIP heterodimer forms
RCD is an umbrella term for any genetically determined signaling a cellular signaling platform named a ripoptosome that usually
11
pathway that results in cellular demise. RCD thus includes both prevents necroptotic signaling (see below) by cleaving RIPK1,
nonimmunogenic apoptosis and immunogenic RN. Fig. 13.5 RIPK3, and Cylindromatosis (CYLD) while not proteolytically
provides an overview of the most important pathways of RCD, activating downstream effector caspases, such as CASP-3, CASP-6,
including caspase-dependent and caspase-independent forms and CASP-7. Should CASP-8 be activated, however, it will form
of RCD. homodimers to activate named downstream caspases, which
induce apoptosis.
CASPASE-DEPENDENT CELL DEATH RIPK1 polyubiquitination represents a major checkpoint for
a cellular decision of either survival or RCD. For this reason, it
Apoptosis is tightly regulated. Inhibitors of apoptosis 1 and 2 (cIAP1/2)
Apoptosis is a complex program for nonimmunogenic cellular and the linear ubiquitination complex (LUBAC) add ubiquitin
demise that is regulated by caspases. During the first hours of chains, whereas OTULIN, CYLD, and A20 remove them. Polyu-
apoptosis, cells maintain their plasma membrane integrity and biquitination is required for NEMO-dependent canonical NF-κB
therefore, by definition, are not necrotic. The apoptotic program signaling and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activa-
may be activated via the intrinsic (mitochondrial) or the extrinsic tion. Both provide a survival signal. In contrast, RCD is licensed
(death receptor) pathways. on loss of polyubiquitination. Remarkably, both pro-survival
The intrinsic pathway is controlled by different members of NF-κB signaling and necroptosis lead to local inflammation,
the Bcl-2 protein family, such as Bcl-2 or BAX, and therefore whereas apoptosis is noninflammatory.
reacts to intracellular changes (e.g., DNA damage) by forming The physiological role of apoptosis has been questioned
transient pores, a process referred to as mitochondrial outer following the observation that CASP-8 deficient mice (which
membrane permeabilization (MOMP). The intrinsic pathway die in utero) can be rescued on a RIPK3-deficient background
reacts to internal stimuli, whereas the default activation of the to become viable and fertile. However, CASP-8 is of critical
extrinsic pathway occurs following an outside-in signaling, typi- importance only for the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, and
cally mediated by death receptors, such as Fas (also known as BAX-/BAK-deficient mice, which cannot undergo intrinsic