Page 72 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 72
CHaPter 4 Antigen Receptor Genes, Gene Products, and Coreceptors 57
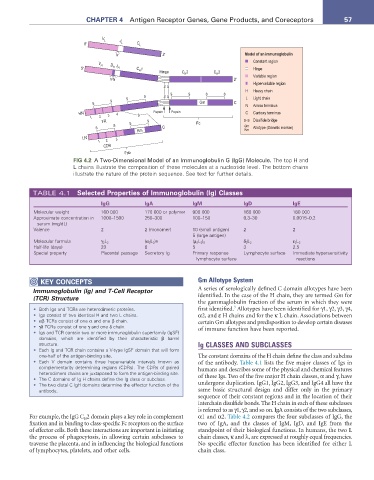
V L
5' J L C L
N 3' Model of an immunoglobulin
Constant region
V H
D H J H
5' C H 1 Hinge
Hinge C 2 C 3
H
H
N N 3' Variable region
Hypervariable region
S S
H Heavy chain
S S S S
S S S L Light chain
S S
S Gm C N Amino terminus
HN 3 4 S Papain Pepsin C Carboxy terminus
1 2
FR S S Fc S–S Disulfide bridge
S S C Gm Allotype (Genetic marker)
Km
Km
LN 3
1 2
CDR
Fab
FIG 4.2 A Two-Dimensional Model of an Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Molecule. The top H and
L chains illustrate the composition of these molecules at a nucleotide level. The bottom chains
illustrate the nature of the protein sequence. See text for further details.
TABLE 4.1 Selected Properties of Immunoglobulin (Ig) Classes
IgG Iga IgM IgD Ige
Molecular weight 160 000 170 000 or polymer 900 000 160 000 180 000
Approximate concentration in 1000–1500 250–300 100–150 0.3–30 0.0015–0.2
serum (mg/dL)
Valence 2 2 (monomer) 10 (small antigen) 2 2
5 (large antigen)
Molecular formula γ 2 L 2 (α 2 L 2 )n (µ 2 L 2 ) 5 δ 2 L 2 ε 2 L 2
Half-life (days) 23 6 5 3 2.5
Special property Placental passage Secretory Ig Primary response Lymphocyte surface Immediate hypersensitivity
lymphocyte surface reactions
KeY ConCePtS Gm Allotype System
Immunoglobulin (Ig) and T-Cell Receptor A series of serologically defined C domain allotypes have been
(TCR) Structure identified. In the case of the H chain, they are termed Gm for
the gammaglobulin fraction of the serum in which they were
3
• Both Igs and TCRs are heterodimeric proteins. first identified. Allotypes have been identified for γ1, γ2, γ3, γ4,
• Igs consist of two identical H and two L chains. α2, and ε H chains and for the κ L chain. Associations between
• αβ TCRs consist of one α and one β chain. certain Gm allotypes and predisposition to develop certain diseases
• γδ TCRs consist of one γ and one δ chain. of immune function have been reported.
• Igs and TCR contain two or more immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF)
domains, which are identified by their characteristic β barrel
structure. Ig CLASSES AND SUBCLASSES
• Each Ig and TCR chain contains a V-type IgSF domain that will form
one-half of the antigen-binding site. The constant domains of the H chain define the class and subclass
• Each V domain contains three hypervariable intervals known as of the antibody. Table 4.1 lists the five major classes of Igs in
complementarity determining regions (CDRs). The CDRs of paired humans and describes some of the physical and chemical features
heterodimers chains are juxtaposed to form the antigen-binding site.
• The C domains of Ig H chains define the Ig class or subclass. of these Igs. Two of the five major H chain classes, α and γ, have
• The two distal C IgH domains determine the effector function of the undergone duplication. IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 all have the
antibody. same basic structural design and differ only in the primary
sequence of their constant regions and in the location of their
interchain disulfide bonds. The H chain in each of these subclasses
is referred to as γ1, γ2, and so on. IgA consists of the two subclasses,
For example, the IgG C H 2 domain plays a key role in complement α1 and α2. Table 4.2 compares the four subclasses of IgG, the
fixation and in binding to class-specific Fc receptors on the surface two of IgA, and the classes of IgM, IgD, and IgE from the
of effector cells. Both these interactions are important in initiating standpoint of their biological functions. In humans, the two L
the process of phagocytosis, in allowing certain subclasses to chain classes, κ and λ, are expressed at roughly equal frequencies.
traverse the placenta, and in influencing the biological functions No specific effector function has been identified for either L
of lymphocytes, platelets, and other cells. chain class.