Page 76 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 76
CHaPter 4 Antigen Receptor Genes, Gene Products, and Coreceptors 61
KeY ConCePtS KeY ConCePtS
Features Common to Immunoglobulin (Ig) and Features Specific to Immunoglobulin (Ig) Genes
T-Cell Receptor (TCR) Genes
• Variable domain somatic hypermutation (SHM) permits affinity matura-
• Ig and TCR variable domains are created by site-specific V(D)J tion, which further diversifies the B-cell repertoire.
recombination. • Class-switch recombination (CSR) allows replacement of an upstream
• Starting with a small set of individual gene segments, combinatorial C domain by a downstream one, altering effector function while
gene segment rearrangement, combinatorial association of heavy and maintaining antigen specificity.
light chains, and mechanisms of junctional diversity generate a broad
repertoire of antigen-binding structures.
• Each receptor is assembled in a stepwise fashion
• Immunoglobulins: D H →J H ; V H →D H J H ; cytoplasmic µ chain expression; that encodes the first three framework regions (FR 1, 2, and 3),
Vκ→Jκ and, if needed, Vλ→Jλ; surface IgM expression. the first two complementarity determining regions in their
• TCRαβ: Dβ→Jβ; Vβ→DβJβ; cytoplasmic β-chain expression; Vα→Jα; entirety, the amino terminal portion of CDR3, and a recombina-
surface αβ TCR expression. tion signal sequence (RSS). A J L (J for joining) gene segment
• Complementarity determining regions (CDRs) 1 and 2 begin with begins with its own recombination signal, the remaining portion
exclusively germline sequence. of CDR 3, and the complete FR 4 (see Fig. 4.2).
• CDR3 is created by the (V[D]J) joining reaction and often includes (Use of the same abbreviation—that is, “V”—for the complete
non-germline N nucleotides between the V and the D, and between
the D and the J. variable domain of an Ig peptide chain as well as the gene segment
• Thus CDR-H3, CDR-B3, and CDR-D3 are the most variable com- that encodes only a portion of that same variable domain is the
ponents of IgM, TCRαβ, and TCRγδ, respectively. result of historic precedent. It is unfortunate that one must depend
• The antigen-binding site is a product of a nested gradient of diversity. on the context of the surrounding text to determine which V
Conserved framework regions surround CDR1 and CDR2, which, in region of the antibody is being discussed. The same holds true
turn, surround the paired CDR3 intervals that form the center of the for the use of “J” to represent both the J gene segment and the
antigen-binding site.
• The variability of the Ig and TCR repertoires is restricted during perinatal J joining protein.)
life, limiting the immune response of the infant. The creation of a V domain is directed by the RSSs that flank
26
the rearranging gene segments. Each RSS contains a strongly
conserved seven base-pair, or heptamer, sequence (e.g., CACAGTG)
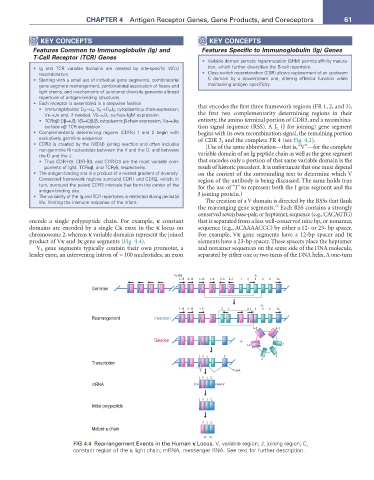
encode a single polypeptide chain. For example, κ constant that is separated from a less well-conserved nine bp, or nonamer,
domains are encoded by a single Cκ exon in the κ locus on sequence (e.g., ACAAAACCC) by either a 12- or 23- bp spacer.
chromosome 2, whereas κ variable domains represent the joined For example, Vκ gene segments have a 12-bp spacer and Jκ
product of Vκ and Jκ gene segments (Fig. 4.4). elements have a 23-bp spacer. These spacers place the heptamer
V L gene segments typically contain their own promoter, a and nonamer sequences on the same side of the DNA molecule,
leader exon, an intervening intron of ≈ 100 nucleotides, an exon separated by either one or two turns of the DNA helix. A one-turn
Vκ (40) Jκ
1–15 3–14 1--12 1–8 5–3 4–1 1 2 3 4 5 Cκ
Germline
Jκ
1–15 3–14 1–8 2 1 4–1 3 4 5 Cκ
Rearrangement Inversion
5–3 4–1
Deletion +
1–8 1
LV J C 2
3
Transcription
AAA
LV JC
mRNA 5' AAA 3'
LV JC
Initial polypeptide
VJ C
Mature κ chain
Vκ Cκ
FIG 4.4 Rearrangement Events in the Human κ Locus. V, variable region; J, joining region; C,
constant region of the κ light chain; mRNA, messenger RNA. See text for further description.