Page 73 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 73
58 Part one Principles of Immune Response
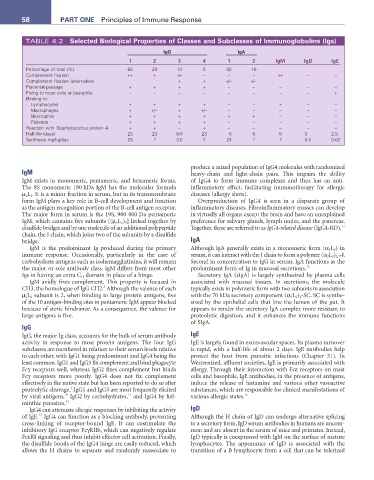
TABLE 4.2 Selected Biological Properties of Classes and Subclasses of Immunoglobulins (Igs)
IgG Iga
1 2 3 4 1 2 IgM IgD Ige
Percentage of total (%) 65 20 10 5 90 10
Complement fixation ++ + ++ − − − ++ − −
Complement fixation (alternative) + + +/− +/−
Placental passage + + + + − − − − −
Fixing to mast cells or basophils − − − − − − − − +
Binding to:
Lymphocytes + + + + − − + − −
Macrophages + +/− + +/− − − − − −
Neutrophils + + + + + + − − −
Platelets + + + + − − − − −
Reaction with Staphylococcus protein A + + − + − − − − −
Half-life (days) 23 23 8-9 23 6 6 5 3 2.5
Synthesis mg/kg/day 25 ? 3.5 ? 24 ? 7 0.4 0.02
produce a mixed population of IgG4 molecules with randomized
IgM heavy-chain and light-chain pairs. This impairs the ability
IgM exists in monomeric, pentameric, and hexameric forms. of IgG4 to form immune complexes and thus has an anti-
The 8S monomeric 180 kDa IgM has the molecular formula inflammatory effect, facilitating immunotherapy for allergic
µ 2 L 2 . It is a minor fraction in serum, but in its transmembrane diseases (allergy shots).
form IgM plays a key role in B-cell development and function Overproduction of IgG4 is seen in a disparate group of
as the antigen recognition portion of the B-cell antigen receptor. inflammatory diseases. Fibroinflammatory masses can develop
The major form in serum is the 19S, 900 000 Da pentameric in virtually all organs except the brain and have an unexplained
IgM, which contains five subunits [(µ 2 L 2 ) 5 ] linked together by preference for salivary glands, lymph nodes, and the pancreas.
disulfide bridges and by one molecule of an additional polypeptide Together, these are referred to as IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). 14
chain, the J chain, which joins two of the subunits by a disulfide
bridge. 7 IgA
IgM is the predominant Ig produced during the primary Although IgA generally exists in a monomeric form (α 2 L 2 ) in
immune response. Occasionally, particularly in the case of serum, it can interact with the J chain to form a polymer (α 2 L 2 ) 2,3 -J.
carbohydrate antigens such as isohemagglutinins, it will remain Second in concentration to IgG in serum, IgA functions as the
the major or sole antibody class. IgM differs from most other predominant form of Ig in mucosal secretions. 15
Igs in having an extra C H domain in place of a hinge. Secretory IgA (sIgA) is largely synthesized by plasma cells
IgM avidly fixes complement. This property is focused in associated with mucosal tissues. In secretions, the molecule
8
CH3, the homologue of IgG CH2. Although the valence of each typically exists in polymeric form with two subunits in association
µ 2 L 2 subunit is 2, when binding to large protein antigens, five with the 70 kDa secretory component (α 2 L 2 ) 2 -SC. SC is synthe-
of the 10 antigen-binding sites in pentameric IgM appear blocked sized by the epithelial cells that line the lumen of the gut. It
because of steric hindrance. As a consequence, the valence for appears to render the secretory IgA complex more resistant to
large antigens is five. proteolytic digestion, and it enhances the immune functions
of SIgA.
IgG
IgG, the major Ig class, accounts for the bulk of serum antibody IgE
activity in response to most protein antigens. The four IgG IgE is largely found in extravascular spaces. Its plasma turnover
subclasses are numbered in relation to their serum levels relative is rapid, with a half-life of about 2 days. IgE antibodies help
to each other, with IgG1 being predominant and IgG4 being the protect the host from parasitic infections (Chapter 31). In
least common. IgG1 and IgG3 fix complement and bind phagocyte Westernized, affluent societies, IgE is primarily associated with
Fcγ receptors well, whereas IgG2 fixes complement but binds allergy. Through their interaction with Fcε receptors on mast
Fcγ receptors more poorly. IgG4 does not fix complement cells and basophils, IgE antibodies, in the presence of antigens,
effectively in the native state but has been reported to do so after induce the release of histamine and various other vasoactive
9
proteolytic cleavage. IgG1 and IgG3 are most frequently elicited substances, which are responsible for clinical manifestations of
11
10
by viral antigens, IgG2 by carbohydrates, and IgG4 by hel- various allergic states. 16
minthic parasites. 12
IgG4 can attenuate allergic responses by inhibiting the activity IgD
13
of IgE. IgG4 can function as a blocking antibody, preventing Although the H chain of IgD can undergo alternative splicing
cross-linking of receptor-bound IgE. It can costimulate the to a secretory form, IgD serum antibodies in humans are uncom-
inhibitory IgG receptor FcγRIIb, which can negatively regulate mon and are absent in the serum of mice and primates. Instead,
FcεRI signaling and thus inhibit effector cell activation. Finally, IgD typically is coexpressed with IgM on the surface of mature
the disulfide bonds of the IgG4 hinge are easily reduced, which lymphocytes. The appearance of IgD is associated with the
allows the H chains to separate and randomly reassociate to transition of a B lymphocyte from a cell that can be tolerized