Page 79 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 79
64 Part one Principles of Immune Response
Combination diversity
4
H
H
39V H x 27D x 6rf x 6J =3.8 x10 Light chain Heavy chain
V CDR-H3
FR H D C FR4 CDR-H1
1 2 3 H J H H
CDR-L2
12
CDR FR3 FR3
(family)
V H N N J H C H
W
FR1 FR1
FR3 FR4 C 1 (Clan)
H
CDR-H3
N - D - N CDR-L1
H
FR4
N region junction diversity CDR-L3 CDR-H2
7
3
3
A 20 x 20 = 6.4 x 10 B
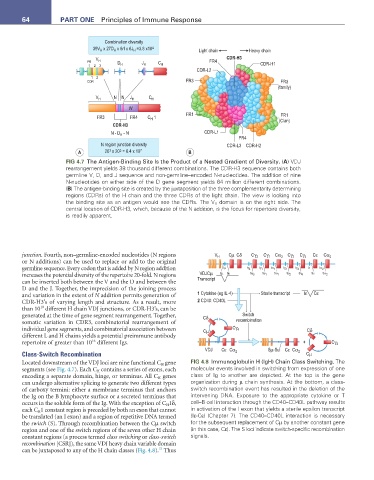
FIG 4.7 The Antigen-Binding Site Is the Product of a Nested Gradient of Diversity. (a) VDJ
rearrangement yields 38 thousand different combinations. The CDR-H3 sequence contains both
germline V, D, and J sequence and non-germline–encoded N-nucleotides. The addition of nine
N-nucleotides on either side of the D gene segment yields 64 million different combinations.
(B) The antigen-binding site is created by the juxtaposition of the three complementarity determining
regions (CDRs) of the H chain and the three CDRs of the light chain. The view is looking into
the binding site as an antigen would see the CDRs. The V H domain is on the right side. The
central location of CDR-H3, which, because of the N addition, is the focus for repertoire diversity,
is readily apparent.
junction. Fourth, non–germline-encoded nucleotides (N regions V H Cµ Cδ Cγ 3 Cγ 1 Cα 3 Cγ 2 Cγ 4 Cε Cα 2
or N additions) can be used to replace or add to the original
germline sequence. Every codon that is added by N region addition Iµ Iγ 3 Iγ 1 Iα 1 Iγ 2 Iγ 4 Iε Iα 2
increases the potential diversity of the repertoire 20-fold. N regions VDJCµ Eµ Sµ Sγ 3 Sγ 1 Sα 1 Sγ 2 Sγ 4 Sε Sα 2
can be inserted both between the V and the D and between the Transcript
D and the J. Together, the imprecision of the joining process
and variation in the extent of N addition permits generation of 1 Cytokine (eg IL-4) Sterile transcript Iε Cε
CDR-H3’s of varying length and structure. As a result, more 2 CD40: CD40L
10
than 10 different H chain VDJ junctions, or CDR-H3’s, can be
generated at the time of gene segment rearrangement. Together, Cδ Switch
somatic variation in CDR3, combinatorial rearrangement of recombination
individual gene segments, and combinatorial association between Cµ Cγ 4 Cδ
different L and H chains yields a potential preimmune antibody
16
repertoire of greater than 10 different Igs. + Cγ 4
VDJ Cε Cα 2 Sµ-Sε Cε Cα 2
Class-Switch Recombination Cµ
Located downstream of the VDJ loci are nine functional C H gene FIG 4.8 Immunoglobulin H (IgH) Chain Class Switching. The
segments (see Fig. 4.7). Each C H contains a series of exons, each molecular events involved in switching from expression of one
encoding a separate domain, hinge, or terminus. All C H genes class of Ig to another are depicted. At the top is the gene
can undergo alternative splicing to generate two different types organization during µ chain synthesis. At the bottom, a class-
of carboxy termini: either a membrane terminus that anchors switch recombination event has resulted in the deletion of the
the Ig on the B lymphocyte surface or a secreted terminus that intervening DNA. Exposure to the appropriate cytokine or T
occurs in the soluble form of the Ig. With the exception of C H 1δ, cell–B cell interaction through the CD40–CD40L pathway results
each C H 1 constant region is preceded by both an exon that cannot in activation of the I exon that yields a sterile epsilon transcript
be translated (an I exon) and a region of repetitive DNA termed (Iε-Cε) (Chapter 7). The CD40–CD40L interaction is necessary
the switch (S). Through recombination between the Cµ switch for the subsequent replacement of Cµ by another constant gene
region and one of the switch regions of the seven other H chain (in this case, Cε). The S loci indicate switch-specific recombination
constant regions (a process termed class switching or class-switch signals.
recombination [CSR]), the same VDJ heavy chain variable domain
33
can be juxtaposed to any of the H chain classes (Fig. 4.8). Thus