Page 83 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 83
68 Part one Principles of Immune Response
in development, Igα and Igβ are coexpressed together with Igs
43
of all isotypes on the surface of B cells as a mature BCR complex.
The CD79 proteins are specific to the B lineage and are expressed AG
throughout B lymphopoiesis. This has led to their use as markers IgH BCR
for the identification of B-cell neoplasms. 46,47
The signaling capacity of both Igα and Igβ resides within an
immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) that IgL
has the consensus sequence of D/IxxYxxL(x)7YxxL, where x is
any amino acid. Similar ITAMs are also found within the
cytoplasmic domain of the molecules that associate with, and Ig-α
signal for, the T-cell antigen receptor (CD3) and certain Fc Ig-β
receptors (Chapter 15). The phosphorylation of both tyrosines
in both Igα/β ITAMs is considered an obligate initial step in the
propagation of antigen receptor engagement to the cell nucleus. 44,48
Tyrosine-phosphorylated ITAMs serve as efficient binding
sites for Src homology 2 (SH2) domains, which are present within
a large number of cytosolic signaling molecules. Whether Igα Syk
and Igβ make qualitatively different contributions toward BCR Lyn
signaling or are functionally redundant remains unclear, as Fyn
evidence exists to support both views. Moreover, the high degree Blk
of evolutionary conservation within the non-ITAM portion of
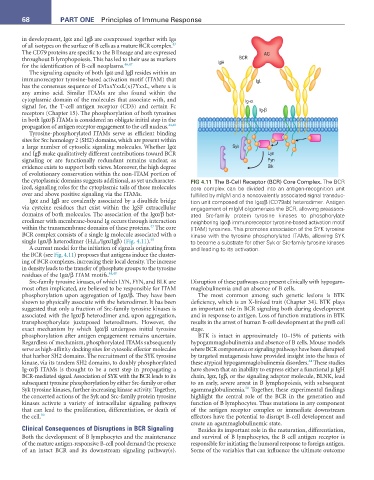
the cytoplasmic domains suggests additional, as yet uncharacter- FIG 4.11 The B-Cell Receptor (BCR) Core Complex. The BCR
ized, signaling roles for the cytoplasmic tails of these molecules core complex can be divided into an antigen-recognition unit
over and above positive signaling via the ITAMs. fulfilled by mIgM and a noncovalently associated signal transduc-
Igα and Igβ are covalently associated by a disulfide bridge tion unit composed of the Igα/β (CD79ab) heterodimer. Antigen
via cysteine residues that exist within the IgSF extracellular engagement of mIgM oligomerizes the BCR, allowing preassoci-
domains of both molecules. The association of the Igα/β het- ated Src-family protein tyrosine kinases to phosphorylate
erodimer with membrane-bound Ig occurs through interaction neighboring Igαβ immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif
43
within the transmembrane domains of these proteins. The core (ITAM) tyrosines. This promotes association of the SYK tyrosine
BCR complex consists of a single Ig molecule associated with a kinase with the tyrosine phosphorylated ITAMs, allowing SYK
single Igα/β heterodimer (H 2 L 2 /Igα/Igβ) (Fig. 4.11). 49 to become a substrate for other Syk or Src-family tyrosine kinases
A current model for the initiation of signals originating from and leading to its activation.
the BCR (see Fig. 4.11) proposes that antigens induce the cluster-
ing of BCR complexes, increasing their local density. The increase
in density leads to the transfer of phosphate groups to the tyrosine
residues of the Igα/β ITAM motifs. 44,48
Src-family tyrosine kinases, of which LYN, FYN, and BLK are Disruption of these pathways can present clinically with hypogam-
most often implicated, are believed to be responsible for ITAM maglobulinemia and an absence of B cells.
phosphorylation upon aggregation of Igα/β. They have been The most common among such genetic lesions is BTK
shown to physically associate with the heterodimer. It has been deficiency, which is an X-linked trait (Chapter 34). BTK plays
suggested that only a fraction of Src-family tyrosine kinases is an important role in BCR signaling both during development
associated with the Igα/β heterodimer and, upon aggregation, and in response to antigen. Loss of function mutations in BTK
transphosphorylate juxtaposed heterodimers. However, the results in the arrest of human B-cell development at the preB cell
exact mechanism by which Igα/β undergoes initial tyrosine stage.
phosphorylation after antigen engagement remains uncertain. BTK is intact in approximately 10–15% of patients with
Regardless of mechanism, phosphorylated ITAMs subsequently hypogammaglobulinemia and absence of B cells. Mouse models
serve as high-affinity docking sites for cytosolic effector molecules where BCR components or signaling pathways have been disrupted
that harbor SH2 domains. The recruitment of the SYK tyrosine by targeted mutagenesis have provided insight into the basis of
44
kinase, via its tandem SH2 domains, to doubly phosphorylated these atypical hypogammaglobulinemia disorders. These studies
Ig-α/β ITAMs is thought to be a next step in propagating a have shown that an inability to express either a functional µ IgH
BCR-mediated signal. Association of SYK with the BCR leads to its chain, Igα, Igβ, or the signaling adaptor molecule, BLNK, lead
subsequent tyrosine phosphorylation by either Src-family or other to an early, severe arrest in B lymphopoiesis, with subsequent
50
Syk tyrosine kinases, further increasing kinase activity. Together, agammaglobulinemia. Together, these experimental findings
the concerted actions of the Syk and Src-family protein tyrosine highlight the central role of the BCR in the generation and
kinases activate a variety of intracellular signaling pathways function of B lymphocytes. Thus mutations in any component
that can lead to the proliferation, differentiation, or death of of the antigen receptor complex or immediate downstream
the cell. 50 effectors have the potential to disrupt B-cell development and
create an agammaglobulinemic state.
Clinical Consequences of Disruptions in BCR Signaling Besides its important role in the maturation, differentiation,
Both the development of B lymphocytes and the maintenance and survival of B lymphocytes, the B cell antigen receptor is
of the mature antigen-responsive B-cell pool demand the presence responsible for initiating the humoral response to foreign antigen.
of an intact BCR and its downstream signaling pathway(s). Some of the variables that can influence the ultimate outcome