Page 790 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 790
CHaPtEr 56 Inflammatory Muscle Diseases 761
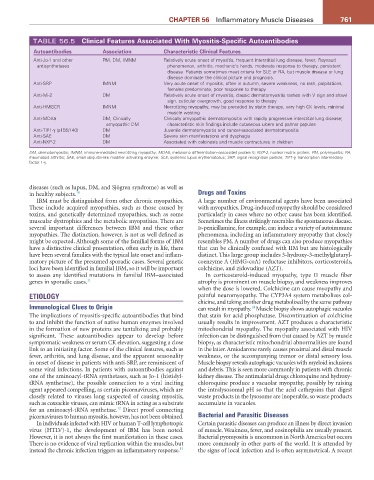
TABLE 56.5 Clinical Features associated With Myositis-Specific autoantibodies
autoantibodies association Characteristic Clinical Features
Anti-Jo-1 and other PM, DM, IMNM Relatively acute onset of myositis, frequent interstitial lung disease, fever, Raynaud
antisynthetases phenomenon, arthritis, mechanic’s hands, moderate response to therapy, persistent
disease. Patients sometimes meet criteria for SLE or RA, but muscle disease or lung
disease dominate the clinical picture and prognosis.
Anti-SRP IMNM Very acute onset of myositis, often in autumn, severe weakness, no rash, palpitations,
females predominate, poor response to therapy
Anti-Mi-2 DM Relatively acute onset of myositis, classic dermatomyositis rashes with V sign and shawl
sign, cuticular overgrowth, good response to therapy
Anti-HMGCR IMNM Necrotizing myopathy, may be preceded by statin therapy, very high CK levels, minimal
muscle wasting
Anti-MDA5 DM, Clinically Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease;
amyopathic DM characteristic skin findings include cutaneous ulcers and palmar papules
Anti-TIF1-γ (p155/140) DM Juvenile dermatomyositis and cancer-associated dermatomyositis
Anti-SAE DM Severe skin manifestations and dysphagia
Anti-NXP-2 DM Associated with calcinosis and muscle contractures in children
DM, dermatomyositis; IMNM, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy; MDA5, melanoma differentiation–associated protein 5; NXP-2, nuclear matrix protein; PM, polymyositis; RA,
rheumatoid arthritis; SAE, small ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SRP, signal recognition particle; TIF1-γ, transcription intermediary
factor 1-γ.
diseases (such as lupus, DM, and Sjögren syndrome) as well as
in healthy subjects. 10 Drugs and Toxins
IBM must be distinguished from other chronic myopathies. A large number of environmental agents have been associated
These include acquired myopathies, such as those caused by with myopathies. Drug-induced myopathy should be considered
toxins, and genetically determined myopathies, such as some particularly in cases where no other cause has been identified.
muscular dystrophies and the metabolic myopathies. There are Sometimes the illness strikingly resembles the spontaneous disease.
several important differences between IBM and these other D-penicillamine, for example, can induce a variety of autoimmune
myopathies. The distinction, however, is not as well defined as phenomena, including an inflammatory myopathy that closely
might be expected. Although some of the familial forms of IBM resembles PM. A number of drugs can also produce myopathies
have a distinctive clinical presentation, often early in life, there that can be clinically confused with IIM but are histologically
have been several families with the typical late onset and inflam- distinct. This large group includes 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-
matory picture of the presumed sporadic cases. Several genetic coenzyme A (HMG-coA) reductase inhibitors, corticosteroids,
loci have been identified in familial IBM, so it will be important colchicine, and zidovudine (AZT).
to assess any identified mutations in familial IBM–associated In corticosteroid-induced myopathy, type II muscle fiber
genes in sporadic cases. 11 atrophy is prominent on muscle biopsy, and weakness improves
when the dose is lowered. Colchicine can cause myopathy and
ETIOLOGY painful neuromyopathy. The CYP3A4 system metabolizes col-
chicine, and taking another drug metabolized by the same pathway
Immunological Clues to Origin can result in myopathy. Muscle biopsy shows autophagic vacuoles
14
The implications of myositis-specific autoantibodies that bind that stain for acid phosphatase. Discontinuation of colchicine
to and inhibit the function of native human enzymes involved usually results in improvement. AZT produces a characteristic
in the formation of new proteins are tantalizing and probably mitochondrial myopathy. The myopathy associated with HIV
significant. These autoantibodies appear to develop before infection can be distinguished from that caused by AZT by muscle
symptomatic weakness or serum CK elevation, suggesting a close biopsy, as characteristic mitochondrial abnormalities are found
link to an initiating factor. Some of the clinical features, such as in the latter. Amiodarone rarely causes proximal and distal muscle
fever, arthritis, and lung disease, and the apparent seasonality weakness, or the accompanying tremor or distal sensory loss.
in onset of disease in patients with anti-SRP, are reminiscent of Muscle biopsy reveals autophagic vacuoles with myeloid inclusions
some viral infections. In patients with autoantibodies against and debris. This is seen more commonly in patients with chronic
one of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, such as Jo-1 (histidyl- kidney disease. The antimalarial drugs chloroquine and hydroxy-
tRNA synthetase), the possible connection to a viral inciting chloroquine produce a vacuolar myopathy, possibly by raising
agent appeared compelling, as certain picornaviruses, which are the intralysosomal pH so that the acid cathepsins that digest
closely related to viruses long suspected of causing myositis, waste products in the lysosome are inoperable, so waste products
such as coxsackie viruses, can mimic tRNA in acting as a substrate accumulate in vacuoles.
12
for an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Direct proof connecting
picornaviruses to human myositis, however, has not been obtained. Bacterial and Parasitic Diseases
In individuals infected with HIV or human T-cell lymphotropic Certain parasitic diseases can produce an illness by direct invasion
virus (HTLV)-1, the development of IBM has been noted. of muscle. Weakness, fever, and eosinophilia are usually present.
However, it is not always the first manifestation in these cases. Bacterial pyomyositis is uncommon in North America but occurs
There is no evidence of viral replication within the muscles, but more commonly in other parts of the world. It is attended by
instead the chronic infection triggers an inflammatory response. 13 the signs of local infection and is often asymmetrical. A recent