Page 90 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 90
CHaPter 4 Antigen Receptor Genes, Gene Products, and Coreceptors 75
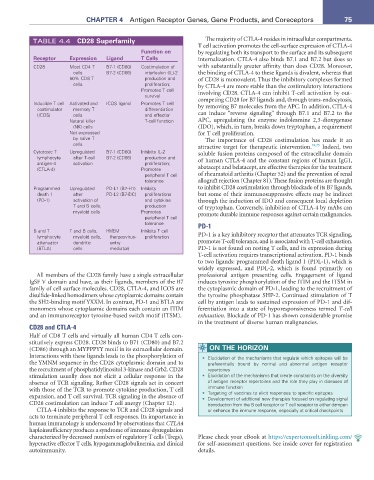
TABLE 4.4 CD28 Superfamily The majority of CTLA-4 resides in intracellular compartments.
T cell activation promotes the cell-surface expression of CTLA-4
Function on by regulating both its transport to the surface and its subsequent
receptor expression Ligand t Cells internalization. CTLA-4 also binds B7.1 and B7.2 but does so
CD28 Most CD4 T B7-1 (CD80) Costimulation of with substantially greater affinity than does CD28. Moreover,
cells B7-2 (CD86) interleukin (IL)-2 the binding of CTLA-4 to these ligands is divalent, whereas that
50% CD8 T production and of CD28 is monovalent. Thus the inhibitory complexes formed
cells proliferation; by CTLA-4 are more stable than the costimulatory interactions
Promotes T cell involving CD28. CTLA-4 can inhibit T-cell activation by out-
survival
Inducible T cell Activated and ICOS ligand Promotes T cell competing CD28 for B7 ligands and, through trans-endocytosis,
by removing B7 molecules from the APC. In addition, CTLA-4
costimulator memory T differentiation
(ICOS) cells and effector can induce “reverse signaling” through B7.1 and B7.2 to the
Natural killer T-cell function APC, upregulating the enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
(NK) cells (IDO), which, in turn, breaks down tryptophan, a requirement
Not expressed for T cell proliferation.
by naïve T The importance of CD28 costimulation has made it an
cells attractive target for therapeutic intervention. 74,75 Indeed, two
Cytotoxic T Upregulated B7-1 (CD80) Inhibits IL-2 soluble fusion proteins composed of the extracellular domain
lymphocyte after T-cell B7-2 (CD86) production and of human CTLA-4 and the constant regions of human IgG1,
antigen-4 activation proliferation;
(CTLA-4) Promotes abatacept and belatacept, are effective therapies for the treatment
peripheral T cell of rheumatoid arthritis (Chapter 52) and the prevention of renal
tolerance allograft rejection (Chapter 81). These fusion proteins are thought
Programmed Upregulated PD-L1 (B7-H1) Inhibits to inhibit CD28 costimulation through blockade of its B7 ligands,
death 1 after PD-L2 (B7-DC) proliferations but some of their immunosuppressive effects may be indirect
(PD-1) activation of and cytokine through the induction of IDO and consequent local depletion
T and B cells, production of tryptophan. Conversely, inhibition of CTLA-4 by mAbs can
myeloid cells Promotes promote durable immune responses against certain malignancies.
peripheral T cell
tolerance PD-1
B and T T and B cells, HVEM Inhibits T cell
lymphocyte myeloid cells, (herpesvirus- proliferation PD-1 is a key inhibitory receptor that attenuates TCR signaling,
attenuator dendritic entry promotes T-cell tolerance, and is associated with T-cell exhaustion.
(BTLA) cells mediator) PD-1 is not found on resting T cells, and its expression during
T-cell activation requires transcriptional activation. PD-1 binds
to two ligands: programmed death ligand 1 (PDL-1), which is
widely expressed, and PDL-2, which is found primarily on
All members of the CD28 family have a single extracellular professional antigen presenting cells. Engagement of ligand
IgSF V domain and have, as their ligands, members of the B7 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the ITIM and the ITSM in
family of cell surface molecules. CD28, CTLA-4, and ICOS are the cytoplasmic domain of PD-1, leading to the recruitment of
disulfide-linked homodimers whose cytoplasmic domains contain the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Continued stimulation of T
the SH2-binding motif YXXM. In contrast, PD-1 and BTLA are cell by antigen leads to sustained expression of PD-1 and dif-
monomers whose cytoplasmic domains each contain an ITIM ferentiation into a state of hyporesponsiveness termed T-cell
and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM). exhaustion. Blockade of PD-1 has shown considerable promise
in the treatment of diverse human malignancies.
CD28 and CTLA-4
Half of CD8 T cells and virtually all human CD4 T cells con-
stitutively express CD28. CD28 binds to B71 (CD80) and B7.2
(CD86) through an MYPPPYY motif in its extracellular domain. on tHe HorIZon
Interactions with these ligands leads to the phosphorylation of • Elucidation of the mechanisms that regulate which epitopes will be
the YMNM sequence in the CD28 cytoplasmic domain and to preferentially bound by normal and abnormal antigen receptor
the recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Grb2. CD28 repertoires
stimulation usually does not elicit a cellular response in the • Elucidation of the mechanisms that create constraints on the diversity
absence of TCR signaling. Rather CD28 signals act in concert of antigen receptor repertoires and the role they play in diseases of
with those of the TCR to promote cytokine production, T cell immune function
expansion, and T cell survival. TCR signaling in the absence of • Targeting of vaccines to elicit responses to specific epitopes
• Development of additional new therapies focused on regulating signal
CD28 costimulation can induce T cell anergy (Chapter 12). transduction from the B cell receptor or T cell receptor to either dampen
CTLA-4 inhibits the response to TCR and CD28 signals and or enhance the immune response, especially at critical checkpoints
acts to terminate peripheral T cell responses. Its importance in
human immunology is underscored by observations that CTLA4
haploinsufficiency produces a syndrome of immune dysregulation
characterized by decreased numbers of regulatory T cells (Tregs), Please check your eBook at https://expertconsult.inkling.com/
hyperactive effector T cells, hypogammaglobulinemia, and clinical for self-assessment questions. See inside cover for registration
autoimmunity. details.