Page 1180 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1180
CHAPTER 86: Intracranial Pressure: Monitoring and Management 817
P 1 P 2
P 1 P 2 P 1 P 2
P = P 2 P > P 2 P >> P 2
1
1
1
Brain tissue shift
Clinical worsening
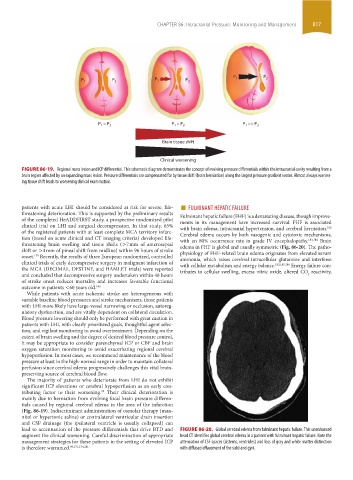
FIGURE 86-19. Regional mass lesion and ICP differential. This schematic diagram demonstrates the concept of evolving pressure differentials within the intracranial cavity resulting from a
brain region affected by an expanding mass lesion. Pressure differentials are compensated for by tissue shift (brain herniation) along the largest pressure gradient vector. Almost always worsen-
ing tissue shift leads to worsening clinical examination.
■
patients with acute LHI should be considered at risk for severe, life- FULMINANT HEPATIC FAILURE
threatening deterioration. This is supported by the preliminary results Fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) is a devastating disease, though improve-
of the completed HeADDFIRST study, a prospective randomized pilot ments in its management have increased survival. FHF is associated
clinical trial on LHI and surgical decompression. In that study, 65% with brain edema, intracranial hypertension, and cerebral herniation.
182
of the registered patients with at least complete MCA territory infarc- Cerebral edema occurs by both vasogenic and cytotoxic mechanisms,
tion (based on acute clinical and CT imaging criteria) developed life- with an 80% occurrence rate in grade IV encephalopathy. 183,184 Brain
threatening brain swelling and tissue shifts (>7 mm of anteroseptal edema in FHF is global and usually symmetric (Fig. 86-20). The patho-
shift or >4 mm of pineal shift from midline) within 96 hours of stroke physiology of FHF-related brain edema originates from elevated serum
onset. Recently, the results of three European randomized, controlled ammonia, which raises cerebral intracellular glutamine and interferes
179
clinical trials of early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of with cellular metabolism and energy balance. 183,185,186 Energy failure con-
the MCA (DECIMAL, DESTINY, and HAMLET trials) were reported tributes to cellular swelling, excess nitric oxide, altered CO reactivity,
and concluded that decompressive surgery undertaken within 48 hours 2
of stroke onset reduces mortality and increases favorable functional
outcome in patients <60 years old. 180
While patients with acute ischemic stroke are heterogeneous with
variable baseline blood pressures and stroke mechanisms, those patients
with LHI more likely have large-vessel narrowing or occlusion, autoreg-
ulatory dysfunction, and are vitally dependent on collateral circulation.
Blood pressure lowering should only be performed with great caution in
patients with LHI, with clearly prioritized goals, thoughtful agent selec-
tion, and vigilant monitoring to avoid overtreatment. Depending on the
extent of brain swelling and the degree of desired blood pressure control,
it may be appropriate to consider parenchymal ICP or CBF and brain
oxygen saturation monitoring to avoid exacerbating regional cerebral
hypoperfusion. In most cases, we recommend maintenance of the blood
pressure at least in the high-normal range in order to maintain collateral
perfusion since cerebral edema progressively challenges this vital brain-
preserving source of cerebral blood flow.
The majority of patients who deteriorate from LHI do not exhibit
significant ICP elevations or cerebral hypoperfusion as an early con-
tributing factor to their worsening. Their clinical deterioration is
99
mainly due to herniation from evolving focal brain pressure differen-
tials caused by regional cerebral edema in the area of the infarction
(Fig. 86-19). Indiscriminant administration of osmolar therapy (man-
nitol or hypertonic saline) or contralateral ventricular drain insertion
and CSF drainage (the ipsilateral ventricle is usually collapsed) can
lead to accentuation of the pressure differentials that drive BTD and FIGURE 86-20. Global cerebral edema from fulminant hepatic failure. This unenhanced
augment the clinical worsening. Careful discrimination of appropriate head CT identifies global cerebral edema in a patient with fulminant hepatic failure. Note the
management strategies for these patients in the setting of elevated ICP attenuation of CSF spaces (cisterns, ventricles) and loss of gray and white matter distinction
is therefore warranted. 99,171,174,181 with diffused effacement of the sulci and gyri.
section06.indd 817 1/23/2015 12:56:14 PM