Page 356 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 356
340 PART 5 ■ Nonmalignant Leukocyte Disorders
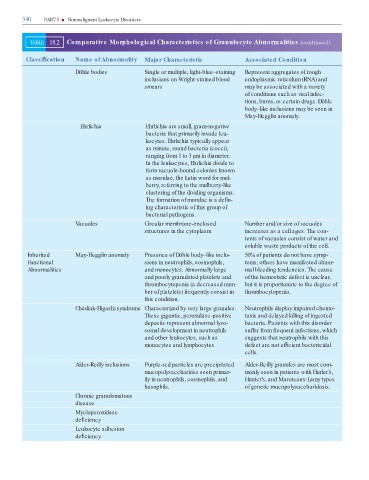
TABLE 18.2 Comparative Morphological Characteristics of Granulocyte Abnormalities (continued)
Classi cation Name of Abnormality Major Characteristic Associated Condition
Döhle bodies Single or multiple, light-blue–staining Represent aggregates of rough
inclusions on Wright-stained blood endoplasmic reticulum (RNA) and
smears may be associated with a variety
of conditions such as viral infec-
tions, burns, or certain drugs. Döhle
body–like inclusions may be seen in
May-Hegglin anomaly.
Ehrlichia Ehrlichia are small, gram-negative
bacteria that primarily invade leu-
kocytes. Ehrlichia typically appear
as minute, round bacteria (cocci),
ranging from 1 to 3 µm in diameter.
In the leukocytes, Ehrlichia divide to
form vacuole-bound colonies known
as morulae, the Latin word for mul-
berry, referring to the mulberry-like
clustering of the dividing organisms.
The formation of morulae is a de n-
ing characteristic of this group of
bacterial pathogens.
Vacuoles Circular membrane-enclosed Number and/or size of vacuoles
structures in the cytoplasm increases as a cell ages. The con-
tents of vacuoles consist of water and
soluble waste products of the cell.
Inherited May-Hegglin anomaly Presence of Döhle body–like inclu- 50% of patients do not have symp-
Functional sions in neutrophils, eosinophils, toms; others have manifested abnor-
Abnormalities and monocytes. Abnormally large mal bleeding tendencies. The cause
and poorly granulated platelets and of the hemostatic defect is unclear,
thrombocytopenia (a decreased num- but it is proportionate to the degree of
ber of platelets) frequently coexist in thrombocytopenia.
this condition.
Chédiak-Higashi syndrome Characterized by very large granules. Neutrophils display impaired chemo-
These gigantic, peroxidase-positive taxis and delayed killing of ingested
deposits represent abnormal lyso- bacteria. Patients with this disorder
somal development in neutrophils suffer from frequent infections, which
and other leukocytes, such as suggests that neutrophils with this
monocytes and lymphocytes defect are not ef cient bactericidal
cells.
Alder-Reilly inclusions Purple-red particles are precipitated Alder-Reilly granules are most com-
mucopolysaccharides seen primar- monly seen in patients with Hurler’s,
ily in neutrophils, eosinophils, and Hunter’s, and Maroteaux-Lamy types
basophils. of genetic mucopolysaccharidosis.
Chronic granulomatous
disease
Myeloperoxidase
de ciency
Leukocyte adhesion
de ciency