Page 643 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 643
CHAPTER 30 ■ Instrumentation in Hematology 627
General Histogram Characteristics
Histograms are graphic representations o cell requencies
versus sizes. In a homogeneous cell population, the curve
assumes a symmetrical bell-shaped or Gaussian distribution.
A wide or more f attened curve is seen when the standard
deviation (SD) rom the mean is increased. Histograms not
only provide in ormation about erythrocyte, leukocyte, and
platelet requency and their distribution about the mean but
also depict the presence o subpopulations.
Histograms provide a means o comparing the sizes o a
patient’s cells with those o normal population’s. Shi s in one
direction or the other can be o diagnostic importance. T e
position o the curve on the x-axis ref ects the cell size. In
the Coulter system, the size (volume in emtoliters) is repre-
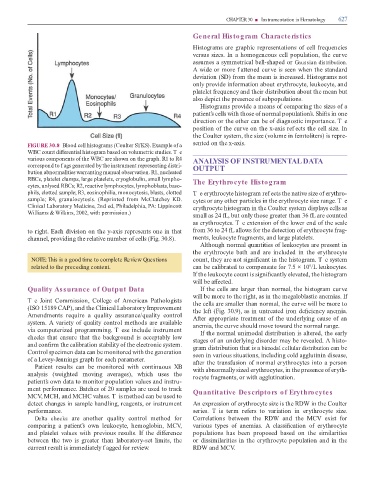
FIGURE 30.8 Blood cell histograms (Coulter S KS). Example o a sented on the x-axis.
WBC count di erential histogram based on volumetric studies. T e
various components o the WBC are shown on the graph. R1 to R4 ANALYSIS OF INSTRUMENTAL DATA
correspond to f ags generated by the instrument representing distri- OUTPUT
bution abnormalities warranting manual observation. R1, nucleated
RBCs, platelet clumps, large platelets, cryoglobulin, small lympho- The Erythrocyte Histogram
cytes, unlysed RBCs; R2, reactive lymphocytes, lymphoblasts, baso-
phils, clotted sample; R3, eosinophilia, monocytosis, blasts, clotted Te erythrocyte histogram ref ects the native size o erythro-
sample; R4, granulocytosis. (Reprinted rom McClatchey KD. cytes or any other particles in the erythrocyte size range. T e
Clinical Laboratory Medicine, 2nd ed, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott erythrocyte histogram in the Coulter system displays cells as
Williams & Wilkins, 2002, with permission.)
small as 24 L, but only those greater than 36 L are counted
as erythrocytes. T e extension o the lower end o the scale
to right. Each division on the y-axis represents one in that rom 36 to 24 L allows or the detection o erythrocyte rag-
channel, providing the relative number o cells (Fig. 30.8). ments, leukocyte ragments, and large platelets.
Although normal quantities o leukocytes are present in
the erythrocyte bath and are included in the erythrocyte
NOTE: This is a good time to complete Review Questions count, they are not signi cant in the histogram. T e system
related to the preceding content. can be calibrated to compensate or 7.5 × 10 /L leukocytes.
9
I the leukocyte count is signi cantly elevated, the histogram
will be a ected.
Quality Assurance of Output Data I the cells are larger than normal, the histogram curve
will be more to the right, as in the megaloblastic anemias. I
T e Joint Commission, College o American Pathologists the cells are smaller than normal, the curve will be more to
(ISO 15189 CAP), and the Clinical Laboratory Improvement the le (Fig. 30.9), as in untreated iron de ciency anemia.
Amendments require a quality assurance/quality control A er appropriate treatment o the underlying cause o an
system. A variety o quality control methods are available anemia, the curve should move toward the normal range.
via computerized programming. T ese include instrument I the normal unimodal distribution is altered, the early
checks that ensure that the background is acceptably low stages o an underlying disorder may be revealed. A histo-
and con rm the calibration stability o the electronic system. gram distribution that is a bimodal cellular distribution can be
Control specimen data can be monitored with the generation seen in various situations, including cold agglutinin disease,
o a Levey-Jennings graph or each parameter. a er the trans usion o normal erythrocytes into a person
Patient results can be monitored with continuous XB with abnormally sized erythrocytes, in the presence o eryth-
analysis (weighted moving averages), which uses the rocyte ragments, or with agglutination.
patient’s own data to monitor population values and instru-
ment per ormance. Batches o 20 samples are used to track Quantitative Descriptors of Erythrocytes
MCV, MCH, and MCHC values. T is method can be used to
detect changes in sample handling, reagents, or instrument An expression o erythrocyte size is the RDW in the Coulter
per ormance. series. T is term re ers to variation in erythrocyte size.
Delta checks are another quality control method or Correlations between the RDW and the MCV exist or
comparing a patient’s own leukocyte, hemoglobin, MCV, various types o anemias. A classi cation o erythrocyte
and platelet values with previous results. I the di erence populations has been proposed based on the similarities
between the two is greater than laboratory-set limits, the or dissimilarities in the erythrocyte population and in the
current result is immediately f agged or review. RDW and MCV.