Page 653 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 653
CHAPTER 30 ■ Instrumentation in Hematology 637
cytoplasmic immunoglobulins (kappa and lambda light
chains, M heavy chain).
Research applications o immunocytochemistry (IC)
immunophenotyping include IC cytokine expression to
examine unctional subtypes o lymphocytes in acquired and
primary immunode ciencies and to measure engra ment
success a er a transplant procedure. Detection o cancer-
related markers in tumors as prognostic indicators (e.g.,
estrogen and progesterone receptors, oncoproteins, p53) is
an additional application.
DNA Ploidy and Cell Cycling
One o the earliest clinical applications o f ow cytometry
was the detection o aneuploidy and cell cycling status o
solid tumors, particularly selected breast tumors. Since 1996, G
the use o DNA analysis has signi cantly decreased. It is now 1
most o en per ormed in patients with node-negative breast S
cancer and other tumors in which the clinical correlation
prognostic signi cance is strongest. Recent technological
i m e 8 or more hours 6-8 hours
innovations may lead to a revival o interest in clinical DNA T i t e G G 2
analysis. f i n e 2 - 5 h o u r s
d 0 M I T O S I S
Because approximately a 2-week lag exists between bone I n
marrow activity and its resultant expression in the peripheral
blood, it is important to assess the current status o the bone T A M P
marrow cells under certain conditions (i.e., cell cycle kinet-
ics). Flow cytometry allows or analysis o the bone marrow
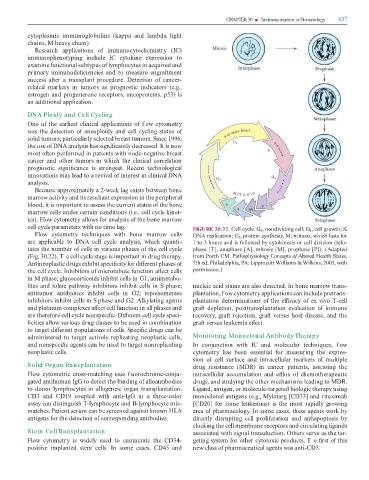
cell cycle parameters with no time lag. FIGURE 30.22 Cell cycle. G , nondividing cell; G , cell growth; S,
1
0
Flow cytometry techniques with bone marrow cells DNA replication; G , protein synthesis; M, mitosis, which lasts or
2
are applicable to DNA cell cycle analysis, which quanti- 1 to 3 hours and is ollowed by cytokinesis or cell division (telo-
tates the number o cells in various phases o the cell cycle phase [ ], anaphase [A], mitosis [M], prophase [P]). (Adapted
(Fig. 30.22). T e cell cycle stage is important in drug therapy. rom Porth CM. Pathophysiology Concepts o Altered Health States,
Antineoplastic drugs exhibit speci city or di erent phases o 7th ed, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005, with
the cell cycle. Inhibitors o microtubule unction a ect cells permission.)
in M phase; glucocorticoids inhibit cells in G1; antimetabo-
lites and olate pathway inhibitors inhibit cells in S phase; nucleic acid stains are also detected. In bone marrow trans-
antitumor antibiotics inhibit cells in G2; topoisomerase plantation, f ow cytometry applications can include pretrans-
inhibitors inhibit cells in S phase and G2. Alkylating agents plantation determinations o the e cacy o ex vivo -cell
and platinum complexes a ect cell unction in all phases and gra depletion, posttransplantation evaluation o immune
are there ore cell cycle nonspeci c. Di erent cell cycle speci- recovery, gra rejection, gra versus host disease, and the
cities allow various drug classes to be used in combination gra versus leukemia e ect.
to target di erent populations o cells. Speci c drugs can be
administered to target actively replicating neoplastic cells, Monitoring Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
and nonspeci c agents can be used to target nonreplicating In conjunction with IC and molecular techniques, f ow
neoplastic cells. cytometry has been essential or measuring the expres-
sion o cell sur ace and intracellular markers o multiple
Solid Organ Transplantation drug resistance (MDR) in cancer patients, assessing the
Flow cytometric cross-matching uses f uorochrome-conju- intracellular accumulation and e ux o chemotherapeutic
gated antihuman IgG to detect the binding o alloantibodies drugs, and studying the other mechanisms leading to MDR.
to donor lymphocytes in allogeneic organ transplantation. Ligand, antigen, or molecule-targeted biologic therapy using
CD3 and CD19 coupled with anti-IgG in a three-color monoclonal antigens (e.g., Mylotarg [CD33] and rituximab
assay can distinguish -lymphocyte and B-lymphocyte mis- [CD20] or some leukemias) is the most rapidly growing
matches. Patient serum can be screened against known HLA area o pharmacology. In some cases, these agents work by
antigens or the detection o corresponding antibodies. directly disrupting cell proli eration and antiapoptosis by
clocking the cell membrane receptors and circulating ligands
Stem Cell Transplantation associated with signal transduction. Others serve as the tar-
Flow cytometry is widely used to enumerate the CD34- geting system or other cytotoxic products. T e rst o this
positive implanted stem cells. In some cases, CD45 and new class o pharmaceutical agents was anti-CD3.