Page 652 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 652
636 PART 8 ■ Fundamentals of Hematological Analysis
and may be used as a guide or timing the administration
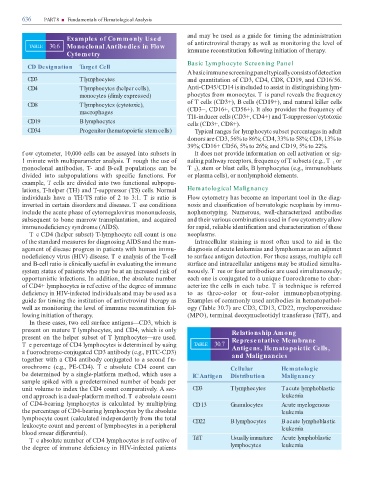
Examples of Commonly Used
TABLE 30.6 Monoclonal Antibodies in Flow o antiretroviral therapy as well as monitoring the level o
immune reconstitution ollowing initiation o therapy.
Cytometry
Basic Lym phocyte Screening Panel
CD Designation Target Cell
A basic immune screening panel typically consists o detection
CD3 T lymphocytes and quantitation o CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, and CD16/56.
CD4 T lymphocytes (helper cells), Anti-CD45/CD14 is included to assist in distinguishing lym-
monocytes (dimly expressed) phocytes rom monocytes. T is panel reveals the requency
o cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+), and natural killer cells
CD8 T lymphocytes (cytotoxic),
macrophages (CD3−, CD16+, CD56+). It also provides the requency o
H-inducer cells (CD3+, CD4+) and -suppressor/cytotoxic
CD19 B lymphocytes cells (CD3+, CD8+).
CD34 Progenitor (hematopoietic stem cells) ypical ranges or lymphocyte subset percentages in adult
donors are CD3, 56% to 86%; CD4, 33% to 58%; CD8, 13% to
39%; CD16+ CD56, 5% to 26%; and CD19, 5% to 22%.
f ow cytometer, 10,000 cells can be assayed into subsets in It does not provide in ormation on cell activation or sig-
1 minute with multiparameter analysis. T rough the use o naling pathway receptors, requency o subsets (e.g., T or
1
monoclonal antibodies, - and B-cell populations can be T ), stem or blast cells, B lymphocytes (e.g., immunoblasts
2
divided into subpopulations with speci c unctions. For or plasma cells), or nonlymphoid elements.
example, cells are divided into two unctional subpopu-
lations, -helper ( H) and -suppressor ( S) cells. Normal Hem atological Malignancy
individuals have a H/ S ratio o 2 to 3:1. T is ratio is Flow cytometry has become an important tool in the diag-
inverted in certain disorders and diseases. T ese conditions nosis and classi cation o hematologic neoplasia by immu-
include the acute phase o cytomegalovirus mononucleosis, nophenotyping. Numerous, well-characterized antibodies
subsequent to bone marrow transplantation, and acquired and their various combinations used in f ow cytometry allow
immunode ciency syndrome (AIDS). or rapid, reliable identi cation and characterization o these
T e CD4 (helper subset) -lymphocyte cell count is one neoplasms.
o the standard measures or diagnosing AIDS and the man- Intracellular staining is most o en used to aid in the
agement o disease progress in patients with human immu- diagnosis o acute leukemias and lymphomas as an adjunct
node ciency virus (HIV) disease. T e analysis o the -cell to sur ace antigen detection. For these assays, multiple cell
and B-cell ratio is clinically use ul in evaluating the immune sur ace and intracellular antigens may be studied simulta-
system status o patients who may be at an increased risk o neously. T ree or our antibodies are used simultaneously;
opportunistic in ections. In addition, the absolute number each one is conjugated to a unique f uorochrome to char-
o CD4+ lymphocytes is ref ective o the degree o immune acterize the cells in each tube. T is technique is re erred
de ciency in HIV-in ected individuals and may be used as a to as three-color or our-color immunophenotyping.
guide or timing the institution o antiretroviral therapy as Examples o commonly used antibodies in hematopathol-
well as monitoring the level o immune reconstitution ol- ogy ( able 30.7) are CD3, CD13, CD22, myeloperoxidase
lowing initiation o therapy. (MPO), terminal deoxynucleotidyl trans erase ( d ), and
In these cases, two cell sur ace antigens—CD3, which is
present on mature lymphocytes, and CD4, which is only Relationship Among
present on the helper subset o lymphocytes—are used. Representative Membrane
T e percentage o CD4 lymphocytes is determined by using TABLE 30.7 Antigens, Hematopoietic Cells,
a f uorochrome-conjugated CD3 antibody (e.g., FI C-CD3) and Malignancies
together with a CD4 antibody conjugated to a second f u-
orochrome (e.g., PE-CD4). T e absolute CD4 count can Cellular Hematologic
be determined by a single-plat orm method, which uses a IC Antigen Distribution Malignancy
sample spiked with a predetermined number o beads per
unit volume to index the CD4 count comparatively. A sec- CD3 T lymphocytes T acute lymphoblastic
ond approach is a dual-plat orm method. T e absolute count leukemia
o CD4-bearing lymphocytes is calculated by multiplying CD 13 Granulocytes Acute myelogenous
the percentage o CD4-bearing lymphocytes by the absolute leukemia
lymphocyte count (calculated independently rom the total CD22 B lymphocytes B acute lymphoblastic
leukocyte count and percent o lymphocytes in a peripheral leukemia
blood smear di erential).
T e absolute number o CD4 lymphocytes is ref ective o TdT Usually immature Acute lymphoblastic
the degree o immune de ciency in HIV-in ected patients lymphocytes leukemia