Page 649 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 649
CHAPTER 30 ■ Instrumentation in Hematology 633
a low pH, the membranes and cytoplasm o speci c leuko-
cytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes
disintegrate and only the bare nuclei remain.
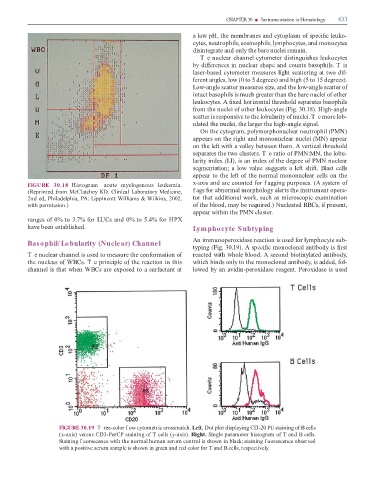
T e nuclear channel cytometer distinguishes leukocytes
by di erences in nuclear shape and counts basophils. T is
laser-based cytometer measures light scattering at two di -
erent angles, low (0 to 5 degrees) and high (5 to 15 degrees).
Low-angle scatter measures size, and the low-angle scatter o
intact basophils is much greater than the bare nuclei o other
leukocytes. A xed horizontal threshold separates basophils
rom the nuclei o other leukocytes (Fig. 30.18). High-angle
scatter is responsive to the lobularity o nuclei. T e more lob-
ulated the nuclei, the larger the high-angle signal.
On the cytogram, polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN)
appears on the right and mononuclear nuclei (MN) appear
on the le with a valley between them. A vertical threshold
separates the two clusters. T e ratio o PMN:MN, the lobu-
larity index (LI), is an index o the degree o PMN nuclear
segmentation; a low value suggests a le shi . Blast cells
appear to the le o the normal mononuclear cells on the
FIGURE 30.18 Histogram—acute myelogenous leukemia. x-axis and are counted or f agging purposes. (A system o
(Reprinted rom McClatchey KD. Clinical Laboratory Medicine, f ags or abnormal morphology alerts the instrument opera-
2nd ed, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2002, tor that additional work, such as microscopic examination
with permission.) o the blood, may be required.) Nucleated RBCs, i present,
appear within the PMN cluster.
ranges o 0% to 3.7% or LUCs and 0% to 5.4% or HPX
have been established. Lymphocyte Subtyping
Basophil/ Lobularity (Nuclear) Channel An immunoperoxidase reaction is used or lymphocyte sub-
typing (Fig. 30.19). A speci c monoclonal antibody is rst
T e nuclear channel is used to measure the con ormation o reacted with whole blood. A second biotinylated antibody,
the nucleus o WBCs. T e principle o the reaction in this which binds only to the monoclonal antibody, is added, ol-
channel is that when WBCs are exposed to a sur actant at lowed by an avidin-peroxidase reagent. Peroxidase is used
FIGURE 30.19 T ree-color f ow cytometric crossmatch. Le . Dot plot displaying CD-20 PE staining o B cells
(x-axis) versus CD3-PerCP staining o cells (y-axis). Right. Single parameter histogram o and B cells.
Staining f uorescence with the normal human serum control is shown in black; staining f uorescence observed
with a positive serum sample is shown in green and red color or and B cells, respectively.