Page 47 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 47
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Lyme disease mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Insect Reservoir mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART I Basic Bacteriology
36
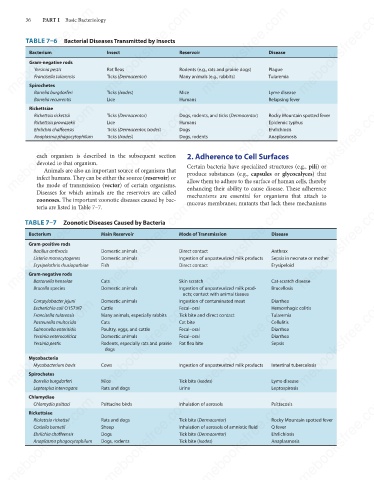
TABLE 7–6 Bacterial Diseases Transmitted by Insects
Bacterium
Disease
Gram-negative rods
Rat fleas
Yersinia pestis
Rodents (e.g., rats and prairie dogs)
Plague
Francisella tularensis
Spirochetes
Mice
Ticks (Ixodes)
Borrelia burgdorferi
Lice
Humans
Relapsing fever
Borrelia recurrentis Ticks (Dermacentor) Many animals (e.g., rabbits) Tularemia
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Ticks (Dermacentor, Ixodes) Dogs mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Rickettsiae
Dogs, rodents, and ticks (Dermacentor)
Rickettsia rickettsii
Ticks (Dermacentor)
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Epidemic typhus
Rickettsia prowazekii
Lice
Humans
Ehrlichia chaffeensis
Ehrlichiosis
Anaplasmosis
Ticks (Ixodes)
Dogs, rodents
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
each organism is described in the subsequent section
2. Adherence to Cell Surfaces
devoted to that organism.
Certain bacteria have specialized structures (e.g., pili) or
Animals are also an important source of organisms that
produce substances (e.g., capsules or glycocalyces) that
infect humans. They can be either the source (reservoir) or
the mode of transmission (vector) of certain organisms.
enhancing their ability to cause disease. These adherence
Diseases for which animals are the reservoirs are called
mechanisms are essential for organisms that attach to
zoonoses. The important zoonotic diseases caused by bac- allow them to adhere to the surface of human cells, thereby
mucous membranes; mutants that lack these mechanisms
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Main Reservoir Mode of Transmission Brucellosis mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
teria are listed in Table 7–7.
TABLE 7–7 Zoonotic Diseases Caused by Bacteria
Disease
Bacterium
Gram-positive rods
Anthrax
Direct contact
Bacillus anthracis
Domestic animals
Domestic animals
Listeria monocytogenes
Sepsis in neonate or mother
Ingestion of unpasteurized milk products
Erysipeloid
Direct contact
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Fish
Gram-negative rods
Cats
Skin scratch
Bartonella henselae
Domestic animals
Ingestion of unpasteurized milk prod-
Brucella species
ucts; contact with animal tissues Cat-scratch disease
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Cats mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Ingestion of contaminated meat
Diarrhea
Campylobacter jejuni
Domestic animals
Cattle
Hemorrhagic colitis
Fecal–oral
Escherichia coli O157:H7
Tularemia
Francisella tularensis
Many animals, especially rabbits
Tick bite and direct contact
Cellulitis
Pasteurella multocida
Cat bite
Poultry, eggs, and cattle
Diarrhea
Fecal–oral
Salmonella enteritidis
Domestic animals
Fecal–oral
Yersinia enterocolitica
Diarrhea
Rodents, especially rats and prairie
Sepsis
Yersinia pestis
Rat flea bite
dogs
Mycobacteria
Ingestion of unpasteurized milk products
Mycobacterium bovis
Cows
Intestinal tuberculosis
Spirochetes
Borrelia burgdorferi
Lyme disease
Tick bite (Ixodes)
Mice
Rats and dogs
Urine
Leptospira interrogans
Leptospirosis
Chlamydiae
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Psittacine birds Inhalation of aerosols Psittacosis mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Chlamydia psittaci
Rickettsiae
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Rats and dogs
Tick bite (Dermacentor)
Rickettsia rickettsii
Q fever
Inhalation of aerosols of amniotic fluid
Coxiella burnetii
Sheep
Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichia chaffeensis
Tick bite (Dermacentor)
Dogs
Anaplasmosis
Tick bite (Ixodes)
Dogs, rodents
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com