Page 51 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 51
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com ADP-R mebooksfree.com space. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
40
PART I Basic Bacteriology
Exotoxins are released from bacteria by specialized
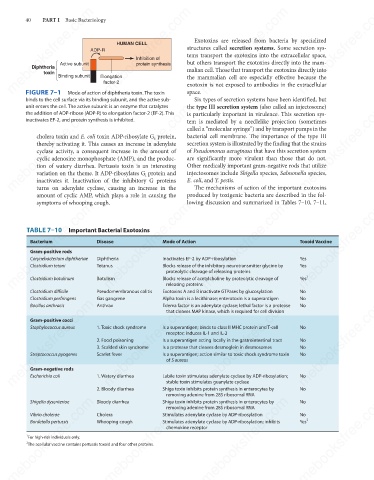
HUMAN CELL
structures called secretion systems. Some secretion sys-
tems transport the exotoxins into the extracellular space,
Inhibition of
but others transport the exotoxins directly into the mam-
protein synthesis
Active subunit
Diphtheria
malian cell. Those that transport the exotoxins directly into
toxin
Binding subunit
Elongation
factor-2
exotoxin is not exposed to antibodies in the extracellular
FIGURE 7–1
Mode of action of diphtheria toxin. The toxin
Six types of secretion systems have been identified, but
binds to the cell surface via its binding subunit, and the active sub- the mammalian cell are especially effective because the
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com called a “molecular syringe”) and by transport pumps in the mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
the type III secretion system (also called an injectosome)
unit enters the cell. The active subunit is an enzyme that catalyzes
the addition of ADP-ribose (ADP-R) to elongation factor-2 (EF-2). This
is particularly important in virulence. This secretion sys-
inactivates EF-2, and protein synthesis is inhibited.
tem is mediated by a needlelike projection (sometimes
bacterial cell membrane. The importance of the type III
cholera toxin and E. coli toxin ADP-ribosylate G protein,
s
secretion system is illustrated by the finding that the strains
thereby activating it. This causes an increase in adenylate
of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that have this secretion system
cyclase activity, a consequent increase in the amount of
are significantly more virulent than those that do not.
cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and the produc-
Other medically important gram-negative rods that utilize
tion of watery diarrhea. Pertussis toxin is an interesting
variation on the theme. It ADP-ribosylates G protein and
i
E. coli, and Y. pestis.
inactivates it. Inactivation of the inhibitory G proteins
The mechanisms of action of the important exotoxins
turns on adenylate cyclase, causing an increase in the
produced by toxigenic bacteria are described in the fol-
amount of cyclic AMP, which plays a role in causing the injectosomes include Shigella species, Salmonella species,
lowing discussion and summarized in Tables 7–10, 7–11,
symptoms of whooping cough.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Disease Mode of Action mebooksfree.com Toxoid Vaccine mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
TABLE 7–10 Important Bacterial Exotoxins
Bacterium
Gram-positive rods
Diphtheria
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Inactivates EF-2 by ADP-ribosylation
Yes
Blocks release of the inhibitory neurotransmitter glycine by
Tetanus
Clostridium tetani
Yes
proteolytic cleavage of releasing proteins
Clostridium botulinum
releasing proteins
Clostridium difficile Botulism Blocks release of acetylcholine by proteolytic cleavage of Yes 1
Pseudomembranous colitis
No
Exotoxins A and B inactivate GTPases by glucosylation
Gas gangrene
No
Alpha toxin is a lecithinase; enterotoxin is a superantigen
Clostridium perfringens
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 1. Toxic shock syndrome Is a superantigen; binds to class II MHC protein and T-cell No mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
No
Bacillus anthracis
Edema factor is an adenylate cyclase; lethal factor is a protease
Anthrax
that cleaves MAP kinase, which is required for cell division
Gram-positive cocci
Staphylococcus aureus
receptor; induces IL-1 and IL-2
No
Is a superantigen acting locally in the gastrointestinal tract
2. Food poisoning
3. Scalded skin syndrome
No
Is a protease that cleaves desmoglein in desmosomes
Is a superantigen; action similar to toxic shock syndrome toxin
Streptococcus pyogenes
Scarlet fever
No
of S aureus
Escherichia coli
stable toxin stimulates guanylate cyclase
No
Gram-negative rods 1. Watery diarrhea Labile toxin stimulates adenylate cyclase by ADP-ribosylation; No
Shiga toxin inhibits protein synthesis in enterocytes by
2. Bloody diarrhea
removing adenine from 28S ribosomal RNA No
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Whooping cough Stimulates adenylate cyclase by ADP-ribosylation; inhibits Yes mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Shigella dysenteriae
Bloody diarrhea
Shiga toxin inhibits protein synthesis in enterocytes by
removing adenine from 28S ribosomal RNA
Vibrio cholerae
No
Stimulates adenylate cyclase by ADP-ribosylation
Cholera
2
Bordetella pertussis
chemokine receptor
1
For high-risk individuals only.
2
The acellular vaccine contains pertussis toxoid and four other proteins.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com