Page 256 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 256
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch09_229-250.indd Page 233 9/3/10 10:07 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch09_229-250.indd Page 233 9/3/10 10:07 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
First Second Third ions. The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged
energy energy energy ions forms ionic bonds, and ionic compounds are the result. In
level level level
general, ionic compounds are formed when a metal from the
left side of the periodic table reacts with a nonmetal from the
right side.
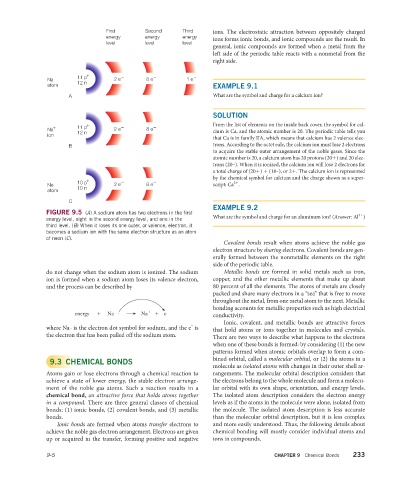
Na 11 p + 2 e – 8 e – 1 e –
atom 12 n EXAMPLE 9.1
A What are the symbol and charge for a calcium ion?
SOLUTION
Na + 11 p + 2 e – 8 e – From the list of elements on the inside back cover, the symbol for cal-
cium is Ca, and the atomic number is 20. The periodic table tells you
ion 12 n
that Ca is in family IIA, which means that calcium has 2 valence elec-
B trons. According to the octet rule, the calcium ion must lose 2 electrons
to acquire the stable outer arrangement of the noble gases. Since the
atomic number is 20, a calcium atom has 20 protons (20+) and 20 elec-
trons (20–). When it is ionized, the calcium ion will lose 2 electrons for
a total charge of (20+) + (18–), or 2+. The calcium ion is represented
2+
Ne 10 p + 2 e – 8 e – by the chemical symbol for calcium and the charge shown as a super-
script: Ca .
atom 10 n
C
EXAMPLE 9.2
FIGURE 9.5 (A) A sodium atom has two electrons in the first 3+
What are the symbol and charge for an aluminum ion? (Answer: Al )
energy level, eight in the second energy level, and one in the
third level. (B) When it loses its one outer, or valence, electron, it
becomes a sodium ion with the same electron structure as an atom
of neon (C).
Covalent bonds result when atoms achieve the noble gas
electron structure by sharing electrons. Covalent bonds are gen-
erally formed between the nonmetallic elements on the right
side of the periodic table.
do not change when the sodium atom is ionized. The sodium Metallic bonds are formed in solid metals such as iron,
ion is formed when a sodium atom loses its valence electron, copper, and the other metallic elements that make up about
and the process can be described by 80 percent of all the elements. The atoms of metals are closely
packed and share many electrons in a “sea” that is free to move
throughout the metal, from one metal atom to the next. Metallic
bonding accounts for metallic properties such as high electrical
energy Na N Na e conductivity.
Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are attractive forces
–
where Na· is the electron dot symbol for sodium, and the e is that hold atoms or ions together in molecules and crystals.
the electron that has been pulled off the sodium atom. There are two ways to describe what happens to the electrons
when one of these bonds is formed: by considering (1) the new
patterns formed when atomic orbitals overlap to form a com-
bined orbital, called a molecular orbital, or (2) the atoms in a
9.3 CHEMICAL BONDS
molecule as isolated atoms with changes in their outer shell ar-
Atoms gain or lose electrons through a chemical reaction to rangements. The molecular orbital description considers that
achieve a state of lower energy, the stable electron arrange- the electrons belong to the whole molecule and form a molecu-
ment of the noble gas atoms. Such a reaction results in a lar orbital with its own shape, orientation, and energy levels.
chemical bond, an attractive force that holds atoms together The isolated atom description considers the electron energy
in a compound. There are three general classes of chemical levels as if the atoms in the molecule were alone, isolated from
bonds: (1) ionic bonds, (2) covalent bonds, and (3) metallic the molecule. The isolated atom description is less accurate
bonds. than the molecular orbital description, but it is less complex
Ionic bonds are formed when atoms transfer electrons to and more easily understood. Thus, the following details about
achieve the noble gas electron arrangement. Electrons are given chemical bonding will mostly consider individual atoms and
up or acquired in the transfer, forming positive and negative ions in compounds.
9-5 CHAPTER 9 Chemical Bonds 233