Page 259 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 259
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch09_229-250.indd Page 236 9/3/10 10:07 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch09_229-250.indd Page 236 9/3/10 10:07 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
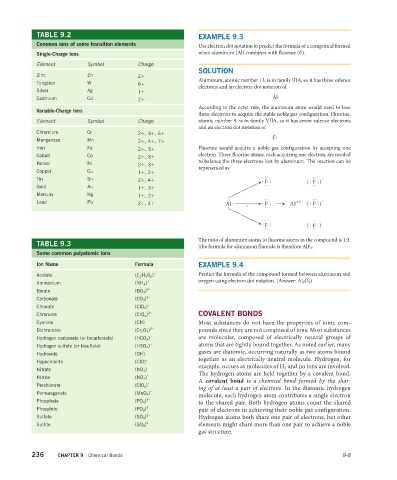
TABLE 9.2 EXAMPLE 9.3
Common ions of some transition elements Use electron dot notation to predict the formula of a compound formed
Single-Charge Ions when aluminum (Al) combines with fluorine (F).
Element Symbol Charge
SOLUTION
Zinc Zn 2+
Aluminum, atomic number 13, is in family IIIA, so it has three valence
Tungsten W 6+
electrons and an electron dot notation of
Silver Ag 1+ ·
Cadmium Cd 2+ Al·
·
According to the octet rule, the aluminum atom would need to lose
Variable-Charge Ions
three electrons to acquire the stable noble gas configuration. Fluorine,
Element Symbol Charge atomic number 9, is in family VIIA, so it has seven valence electrons
and an electron dot notation of
Chromium Cr 2+, 3+, 6+
·F ¨
Manganese Mn 2+, 4+, 7+ ¨ ˙ ˙
Iron Fe 2+, 3+ Fluorine would acquire a noble gas configuration by accepting one
Cobalt Co 2+, 3+ electron. Three fluorine atoms, each acquiring one electron, are needed
to balance the three electrons lost by aluminum. The reaction can be
Nickel Ni 2+, 3+
represented as
Copper Cu 1+, 2+
Tin Sn 2+, 4+ N O (F) S
S O
F S
Q
Q
Gold Au 1+, 3+
Mercury Hg 1+, 2+
S O
Lead Pb 2+, 4+ Al N F O S Al 3 (F) S
P T
Q
Q
R
S O
N O (F) S
F S
Q
Q
The ratio of aluminum atoms to fluorine atoms in the compound is 1:3.
TABLE 9.3 The formula for aluminum fluoride is therefore AlF 3 .
Some common polyatomic ions
Ion Name Formula EXAMPLE 9.4
Acetate (C 2 H 3 O 2 ) – Predict the formula of the compound formed between aluminum and
Ammonium (NH 4 ) + oxygen using electron dot notation. (Answer: Al 2 O 3 )
Borate (BO 3 ) 3–
Carbonate (CO 3 ) 2–
Chlorate (ClO 3 ) –
Chromate (CrO 4 ) 2– COVALENT BONDS
Cyanide (CN) – Most substances do not have the properties of ionic com-
Dichromate (Cr 2 O 7 ) 2– pounds since they are not composed of ions. Most substances
Hydrogen carbonate (or bicarbonate) (HCO 3 ) – are molecular, composed of electrically neutral groups of
Hydrogen sulfate (or bisulfate) (HSO 4 ) – atoms that are tightly bound together. As noted earlier, many
Hydroxide (OH) – gases are diatomic, occurring naturally as two atoms bound
Hypochlorite (ClO) – together as an electrically neutral molecule. Hydrogen, for
example, occurs as molecules of H 2 and no ions are involved.
–
Nitrate (NO 3 )
The hydrogen atoms are held together by a covalent bond.
Nitrite (NO 2 ) –
A covalent bond is a chemical bond formed by the shar-
Perchlorate (ClO 4 ) –
ing of at least a pair of electrons. In the diatomic hydrogen
Permanganate (MnO 4 ) –
molecule, each hydrogen atom contributes a single electron
Phosphate (PO 4 ) 3– to the shared pair. Both hydrogen atoms count the shared
Phosphite (PO 3 ) 3– pair of electrons in achieving their noble gas configuration.
Sulfate (SO 4 ) 2– Hydrogen atoms both share one pair of electrons, but other
Sulfite (SO 3 ) 2– elements might share more than one pair to achieve a noble
gas structure.
236 CHAPTER 9 Chemical Bonds 9-8