Page 334 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 334
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 311 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 311 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
These liquid esters can be obtained from natural sources, or they PROTEINS
can be chemically synthesized. Whatever the source, amyl acetate, Proteins are macromolecular polymers made up of smaller
for example, is the chemical responsible for what you identify as molecules called amino acids. These very large macromolecules
the flavor of banana. Natural flavors, however, are complex mix- have molecular weights that vary from about 6,000 to 50 mil-
tures of these esters along with other organic compounds. Lower lion. Some proteins are simple straight-chain polymers of amino
2+
molecular weight esters are fragrant-smelling liquids, but higher acids, but others contain metal ions such as Fe or parts of or-
molecular weight esters are odorless oils and fats. ganic molecules derived from vitamins. Proteins serve as major
structural and functional materials in living things. Structurally,
proteins are major components of muscles, connective tissue,
CONCEPTS Applied and the skin, hair, and nails. Functionally, some proteins are
enzymes, which catalyze metabolic reactions; hormones, which
Organic Products regulate body activities; hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to
Pick a household product that has ingredients that sound cells; and antibodies, which protect the body.
like they could be organic compounds. On a separate sheet Proteins are formed from 20 amino acids, which are or-
of paper, write the brand name of the product and the type ganic molecules with acid and amino functional groups with
of product (example: Oil of Olay; skin moisturizer), then the general formula of
make a list of the ingredients (column 1). In a second
column beside each name, put the type of compound if you H O
can figure it out from its name or find it in any reference
(example: cetyl palmitate—an ester of cetyl alcohol and R C C OH
palmitic acid). In a third column, put the structural formula
if you can figure it out or find it in any reference such as NH 2
alpha
a CRC handbook or the Merck Index. Finally, in a fourth
column, put whatever you know or can find out about the Note the carbon atom labeled “alpha” in the general formula.
function of that substance in the product.
The amino functional group (NH 2 ) is attached to this carbon
atom, which is next to the carboxylic group (COOH). This
arrangement is called an alpha-amino acid, and the building
blocks of proteins are all alpha-amino acids. The 20 amino acids
differ in the nature of the R group, also called the side chain. It
12.5 ORGANIC COMPOUNDS OF LIFE
is the linear arrangements of amino acids and their side chains
The chemical processes regulated by living organisms begin that determine the properties of a protein.
with relatively small organic molecules and water. The organ- Amino acids are linked to form a protein by a peptide bond
ism uses energy and matter from the surroundings to build between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl
large macromolecules. A macromolecule is a very large mol- group of a second amino acid. A polypeptide is a polymer formed
ecule that is a combination of many smaller, similar molecules from linking many amino acid molecules. If the poly peptide is in-
joined together in a chainlike structure. Macro molecules volved in a biological structure or function, it is called a protein. A
have molecular weights of thousands or millions of atomic protein chain can consist of different combinations of the 20 amino
mass units. There are four main types of macromolecules: acids with hundreds or even thousands of amino acid molecules
(1) proteins, (2) carbohydrates, (3) fats and oils, and (4) nucleic held together with peptide bonds (Figure 12.19). The arrangement
acids. A living organism, even a single-cell organism such as
a bacterium, contains 6,000 or so different kinds of macro-
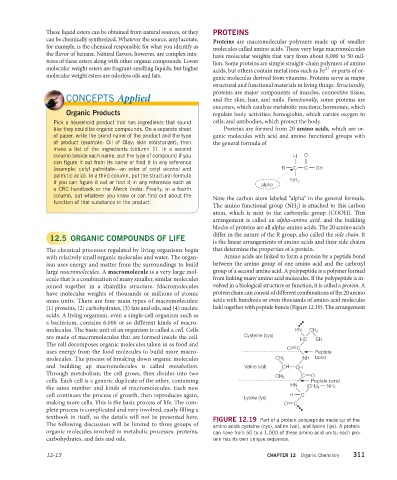
molecules. The basic unit of an organism is called a cell. Cells HN CH 2
are made of macromolecules that are formed inside the cell. Cysteine (cys) HC SH
The cell decomposes organic molecules taken in as food and
O C
uses energy from the food molecules to build more macro- Peptide
molecules. The process of breaking down organic molecules CH 3 NH bond
and building up macromolecules is called metabolism. Valine (val) CH CH
Through metabolism, the cell grows, then divides into two C O
CH 3
cells. Each cell is a generic duplicate of the other, containing Peptide bond
HN
the same number and kinds of macromolecules. Each new (CH 2 ) 4 NH 2
cell continues the process of growth, then reproduces again, H C
Lysine (lys)
making more cells. This is the basic process of life. The com- O C
plete process is complicated and very involved, easily filling a
textbook in itself, so the details will not be presented here.
FIGURE 12.19 Part of a protein polypeptide made up of the
The following discussion will be limited to three groups of amino acids cysteine (cys), valine (val), and lysine (lys). A protein
organic molecules involved in metabolic processes: proteins, can have from 50 to a 1,000 of these amino acid units; each pro-
carbohydrates, and fats and oils. tein has its own unique sequence.
12-13 CHAPTER 12 Organic Chemistry 311