Page 332 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 332
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 309 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 309 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
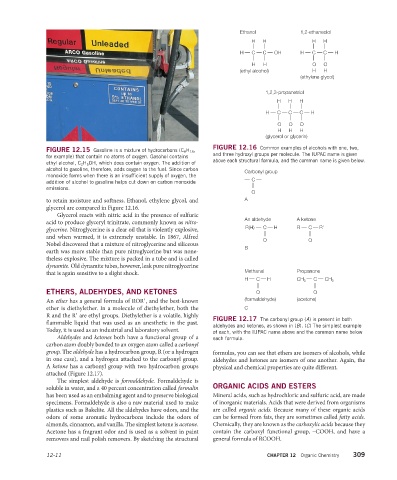
Ethanol 1,2-ethanediol
H H H H
H C C OH H C C H
H H O O
(ethyl alcohol) H H
(ethylene glycol)
1,2,3-propanetriol
H H H
H C C C H
O O O
H H H
(glycerol or glycerin)
FIGURE 12.16 Common examples of alcohols with one, two,
FIGURE 12.15 Gasoline is a mixture of hydrocarbons (C 8 H 18 ,
for example) that contain no atoms of oxygen. Gasohol contains and three hydroxyl groups per molecule. The IUPAC name is given
above each structural formula, and the common name is given below.
ethyl alcohol, C 2 H 5 OH, which does contain oxygen. The addition of
alcohol to gasoline, therefore, adds oxygen to the fuel. Since carbon
Carbonyl group
monoxide forms when there is an insufficient supply of oxygen, the
C
addition of alcohol to gasoline helps cut down on carbon monoxide
emissions.
O
to retain moisture and softness. Ethanol, ethylene glycol, and A
glycerol are compared in Figure 12.16.
Glycerol reacts with nitric acid in the presence of sulfuric
An aldehyde A ketone
acid to produce glyceryl trinitrate, commonly known as nitro-
glycerine. Nitroglycerine is a clear oil that is violently explosive, R(H) C H R C R'
and when warmed, it is extremely unstable. In 1867, Alfred
O O
Nobel discovered that a mixture of nitroglycerine and siliceous
B
earth was more stable than pure nitroglycerine but was none-
theless explosive. The mixture is packed in a tube and is called
dynamite. Old dynamite tubes, however, leak pure nitroglycerine
that is again sensitive to a slight shock. Methanal Propanone
H C H CH 3 C CH 3
ETHERS, ALDEHYDES, AND KETONES O O
An ether has a general formula of ROR′, and the best-known (formaldehyde) (acetone)
ether is diethylether. In a molecule of diethylether, both the C
R and the R′ are ethyl groups. Diethylether is a volatile, highly
FIGURE 12.17 The carbonyl group (A) is present in both
flammable liquid that was used as an anesthetic in the past.
aldehydes and ketones, as shown in (B). (C) The simplest example
Today, it is used as an industrial and laboratory solvent. of each, with the IUPAC name above and the common name below
Aldehydes and ketones both have a functional group of a each formula.
carbon atom doubly bonded to an oxygen atom called a carbonyl
group. The aldehyde has a hydrocarbon group, R (or a hydrogen formulas, you can see that ethers are isomers of alcohols, while
in one case), and a hydrogen attached to the carbonyl group. aldehydes and ketones are isomers of one another. Again, the
A ketone has a carbonyl group with two hydrocarbon groups physical and chemical properties are quite different.
attached (Figure 12.17).
The simplest aldehyde is formaldehyde. Formaldehyde is
soluble in water, and a 40 percent concentration called formalin ORGANIC ACIDS AND ESTERS
has been used as an embalming agent and to preserve biological Mineral acids, such as hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, are made
specimens. Formaldehyde is also a raw material used to make of inorganic materials. Acids that were derived from organisms
plastics such as Bakelite. All the aldehydes have odors, and the are called organic acids. Because many of these organic acids
odors of some aromatic hydrocarbons include the odors of can be formed from fats, they are sometimes called fatty acids.
almonds, cinnamon, and vanilla. The simplest ketone is acetone. Chemically, they are known as the carboxylic acids because they
Acetone has a fragrant odor and is used as a solvent in paint contain the carboxyl functional group, –COOH, and have a
removers and nail polish removers. By sketching the structural general formula of RCOOH.
12-11 CHAPTER 12 Organic Chemistry 309