Page 333 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 333
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 310 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 310 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
Science and Society
Aspirin, a Common Organic Compound
spirin went on the market as a pre- chewed the bark for its medicinal effect. It
QUESTIONS TO DISCUSS
Ascription drug in 1897 after being is estimated that more than 80 million tab-
discovered only two years earlier! How- lets of aspirin are consumed in the United 1. What structural parts of aspirin would
ever, even primitive humans were familiar States daily. It is the most widely used drug make it an organic acid?
with its value as a pain reliever. The bark in the world. Just what does it do? Aspirin is 2. Go to the Internet and find out just
of the willow tree was known for its “magi- really acetylsalicylic acid, which inhibits the how this organic compound acts as a
cal” pain relief power thousands of years body’s production of compounds known as pain reliever.
ago. People in many cultures stripped and prostaglandins, the cause of the pain.
The simplest carboxylic acid has been known since the
Middle Ages, when it was isolated by the distillation of ants.
The Latin word formica means “ant,” so this acid was given the
name formic acid (Figure 12.18). Formic acid is
H O C O OH
B
O
It is formic acid, along with other irritating materials, that causes
the sting of bees, ants, and certain plants such as the stinging nettle.
Acetic acid, the acid of vinegar, has been known since antiq-
uity. Acetic acid forms from the oxidation of ethanol. An oxidized
bottle of wine contains acetic acid in place of the alcohol, which
gives the wine a vinegar taste. Before wine is served in a restaurant,
the person ordering is customarily handed the bottle cork and a
glass with a small amount of wine. You first break the cork in half
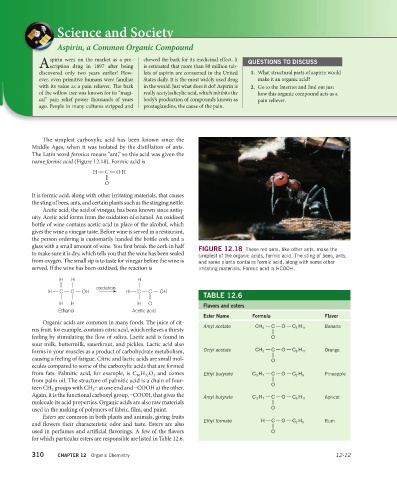
FIGURE 12.18 These red ants, like other ants, make the
to make sure it is dry, which tells you that the wine has been sealed simplest of the organic acids, formic acid. The sting of bees, ants,
from oxygen. The small sip is to taste for vinegar before the wine is and some plants contains formic acid, along with some other
served. If the wine has been oxidized, the reaction is irritating materials. Formic acid is HCOOH.
H H H
oxidation
H C C OH H C C OH
TABLE 12.6
H H H O
Flavors and esters
Ethanol Acetic acid
Ester Name Formula Flavor
Organic acids are common in many foods. The juice of cit-
Amyl acetate CH 3 C O C 5 H 11 Banana
rus fruit, for example, contains citric acid, which relieves a thirsty
feeling by stimulating the flow of saliva. Lactic acid is found in O
sour milk, buttermilk, sauerkraut, and pickles. Lactic acid also
forms in your muscles as a product of carbohydrate metabolism, Octyl acetate CH 3 C O C 8 H 17 Orange
causing a feeling of fatigue. Citric and lactic acids are small mol- O
ecules compared to some of the carboxylic acids that are formed
from fats. Palmitic acid, for example, is C 16 H 32 O 2 and comes Ethyl butyrate C 3 H 7 C O C 2 H 5 Pineapple
from palm oil. The structure of palmitic acid is a chain of four-
O
teen CH 2 groups with CH 3 – at one end and –COOH at the other.
Again, it is the functional carboxyl group, –COOH, that gives the Amyl butyrate C 3 H 7 C O C 5 H 11 Apricot
molecule its acid properties. Organic acids are also raw materials
O
used in the making of polymers of fabric, film, and paint.
Esters are common in both plants and animals, giving fruits
Ethyl formate H C O C 2 H 5 Rum
and flowers their characteristic odor and taste. Esters are also
used in perfumes and artificial flavorings. A few of the flavors O
for which particular esters are responsible are listed in Table 12.6.
310 CHAPTER 12 Organic Chemistry 12-12