Page 446 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 446
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch16_405-432.indd Page 423 9/3/10 6:19 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch16_405-432.indd Page 423 9/3/10 6:19 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
away from Earth’s center toward the Moon. As a result, both
bodies act as a system, moving around a center of mass. The
center of mass between Earth and the Moon follows a smooth
orbit around the Sun. Earth follows a slightly wavy path around
the Sun as it slowly revolves around the common center of mass
(Figure 16.28B).
PHASES OF THE MOON
To the Sun
The phases of the Moon are a result of the changing relative
positions of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun as the Earth-Moon
system moves around the Sun. Sunlight always illuminates one-
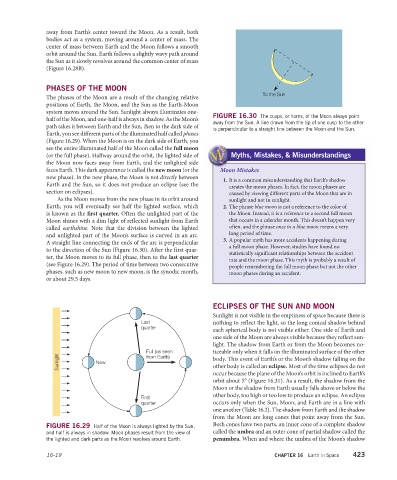
FIGURE 16.30 The cusps, or horns, of the Moon always point
half of the Moon, and one-half is always in shadow. As the Moon’s
away from the Sun. A line drawn from the tip of one cusp to the other
path takes it between Earth and the Sun, then to the dark side of
is perpendicular to a straight line between the Moon and the Sun.
Earth, you see different parts of the illuminated half called phases
(Figure 16.29). When the Moon is on the dark side of Earth, you
see the entire illuminated half of the Moon called the full moon
(or the full phase). Halfway around the orbit, the lighted side of Myths, Mistakes, & Misunderstandings
the Moon now faces away from Earth, and the unlighted side
faces Earth. This dark appearance is called the new moon (or the Moon Mistakes
new phase). In the new phase, the Moon is not directly between
1. It is a common misunderstanding that Earth’s shadow
Earth and the Sun, so it does not produce an eclipse (see the creates the moon phases. In fact, the moon phases are
section on eclipses). caused by viewing different parts of the Moon that are in
As the Moon moves from the new phase in its orbit around sunlight and not in sunlight.
Earth, you will eventually see half the lighted surface, which 2. The phrase blue moon is not a reference to the color of
is known as the fi rst quarter. Often the unlighted part of the the Moon. Instead, it is a reference to a second full moon
Moon shines with a dim light of reflected sunlight from Earth that occurs in a calendar month. This doesn’t happen very
called earthshine. Note that the division between the lighted often, and the phrase once in a blue moon means a very
and unlighted part of the Moon’s surface is curved in an arc. long period of time.
3. A popular myth has more accidents happening during
A straight line connecting the ends of the arc is perpendicular
a full moon phase. However, studies have found no
to the direction of the Sun (Figure 16.30). After the first quar-
statistically significant relationships between the accident
ter, the Moon moves to its full phase, then to the last quarter
rate and the moon phase. This myth is probably a result of
(see Figure 16.29). The period of time between two consecutive people remembering the full moon phase but not the other
phases, such as new moon to new moon, is the synodic month, moon phases during an accident.
or about 29.5 days.
ECLIPSES OF THE SUN AND MOON
Sunlight is not visible in the emptiness of space because there is
Last nothing to reflect the light, so the long conical shadow behind
quarter
each spherical body is not visible either. One side of Earth and
one side of the Moon are always visible because they reflect sun-
light. The shadow from Earth or from the Moon becomes no-
Full (as seen ticeable only when it falls on the illuminated surface of the other
Sunlight New from Earth) body. This event of Earth’s or the Moon’s shadow falling on the
other body is called an eclipse. Most of the time eclipses do not
occur because the plane of the Moon’s orbit is inclined to Earth’s
orbit about 5° (Figure 16.31). As a result, the shadow from the
Moon or the shadow from Earth usually falls above or below the
First other body, too high or too low to produce an eclipse. An eclipse
quarter occurs only when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are in a line with
one another (Table 16.2). The shadow from Earth and the shadow
from the Moon are long cones that point away from the Sun.
Both cones have two parts, an inner cone of a complete shadow
FIGURE 16.29 Half of the Moon is always lighted by the Sun,
and half is always in shadow. Moon phases result from the view of called the umbra and an outer cone of partial shadow called the
the lighted and dark parts as the Moon revolves around Earth. penumbra. When and where the umbra of the Moon’s shadow
16-19 CHAPTER 16 Earth in Space 423