Page 444 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 444
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch16_405-432.indd Page 421 9/3/10 6:19 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch16_405-432.indd Page 421 9/3/10 6:19 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
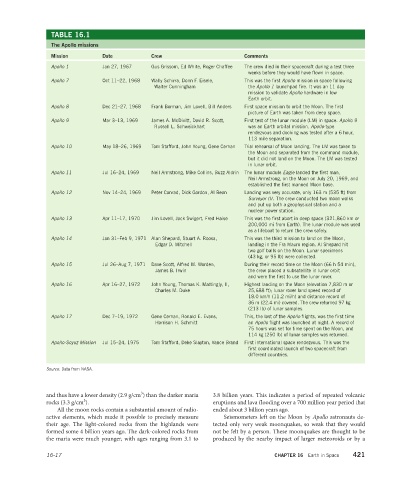
TABLE 16.1
The Apollo missions
Mission Date Crew Comments
Apollo 1 Jan 27, 1967 Gus Grissom, Ed White, Roger Chaffee The crew died in their spacecraft during a test three
weeks before they would have flown in space.
Apollo 7 Oct 11–22, 1968 Wally Schirra, Donn F. Eisele, This was the first Apollo mission in space following
Walter Cunningham the Apollo 1 launchpad fire. It was an 11 day
mission to validate Apollo hardware in low
Earth orbit.
Apollo 8 Dec 21–27, 1968 Frank Borman, Jim Lovell, Bill Anders First space mission to orbit the Moon. The first
picture of Earth was taken from deep space.
Apollo 9 Mar 3–13, 1969 James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, First test of the lunar module (LM) in space. Apollo 9
Russell L. Schweickhart was an Earth orbital mission. Apollo-type
rendezvous and docking was tested after a 6 hour,
113 mile separation.
Apollo 10 May 18–26, 1969 Tom Stafford, John Young, Gene Cernan Trial rehearsal of Moon landing. The LM was taken to
the Moon and separated from the command module,
but it did not land on the Moon. The LM was tested
in lunar orbit.
Apollo 11 Jul 16–24, 1969 Neil Armstrong, Mike Collins, Buzz Aldrin The lunar module Eagle landed the first man,
Neil Armstrong, on the Moon on July 20, 1969, and
established the first manned Moon base.
Apollo 12 Nov 14–24, 1969 Peter Conrad, Dick Gordon, Al Bean Landing was very accurate, only 163 m (535 ft) from
Surveyor III. The crew conducted two moon walks
and put up both a geophysical station and a
nuclear power station.
Apollo 13 Apr 11–17, 1970 Jim Lovell, Jack Swigert, Fred Haise This was the first abort in deep space (321,860 km or
200,000 mi from Earth). The lunar module was used
as a lifeboat to return the crew safely.
Apollo 14 Jan 31–Feb 9, 1971 Alan Shepard, Stuart A. Roosa, This was the third mission to land on the Moon,
Edgar D. Mitchell landing in the Fra Mauro region. Al Shepard hit
two golf balls on the Moon. Lunar specimens
(43 kg, or 95 lb) were collected.
Apollo 15 Jul 26–Aug 7, 1971 Dave Scott, Alfred M. Worden, During their record time on the Moon (66 h 54 min),
James B. Irwin the crew placed a subsatellite in lunar orbit
and were the first to use the lunar rover.
Apollo 16 Apr 16–27, 1972 John Young, Thomas K. Mattingly, II, Highest landing on the Moon (elevation 7,830 m or
Charles M. Duke 25,688 ft); lunar rover land speed record of
18.0 km/h (11.2 mi/h) and distance record of
36 m (22.4 mi) covered. The crew returned 97 kg
(213 lb) of lunar samples.
Apollo 17 Dec 7–19, 1972 Gene Cernan, Ronald E. Evans, This, the last of the Apollo flights, was the first time
Harrison H. Schmitt an Apollo flight was launched at night. A record of
75 hours was set for time spent on the Moon, and
114 kg (250 lb) of lunar samples was returned.
Apollo-Soyuz Mission Jul 15–24, 1975 Tom Stafford, Deke Slayton, Vance Brand First international space rendezvous. This was the
first coordinated launch of two spacecraft from
different countries.
Source: Data from NASA.
3
and thus have a lower density (2.9 g/cm ) than the darker maria 3.8 billion years. This indicates a period of repeated volcanic
3
rocks (3.3 g/cm ). eruptions and lava flooding over a 700 million year period that
All the moon rocks contain a substantial amount of radio- ended about 3 billion years ago.
active elements, which made it possible to precisely measure Seismometers left on the Moon by Apollo astronauts de-
their age. The light-colored rocks from the highlands were tected only very weak moonquakes, so weak that they would
formed some 4 billion years ago. The dark-colored rocks from not be felt by a person. These moonquakes are thought to be
the maria were much younger, with ages ranging from 3.1 to produced by the nearby impact of larger meteoroids or by a
16-17 CHAPTER 16 Earth in Space 421